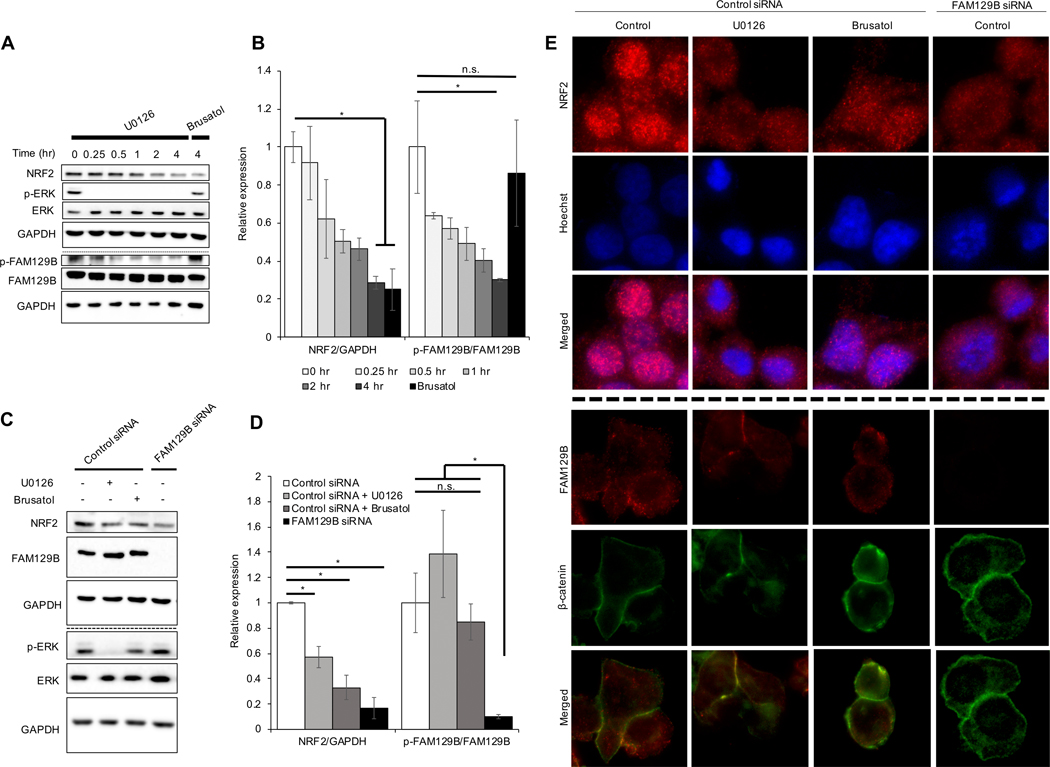
Figure 3: FAM129B knockdown or pharmacologically induced membrane localization decreases NRF2 protein levels.
(A) A375 cells were treated with 10 μM U0126 for 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 hr or 40 nM brusatol for 4 hr and then subjected to immunoblot analysis of NRF2, p-ERK, ERK, p-FAM129B, and FAM129B. (B) Protein levels of NRF2/GAPDH and p-FAM129B/FAM129B were quantified from immunoblot analyses in (A) (n=3). (C) At 72 hr post siRNA transfection, cells were treated with 10 μM U0126 or 40 nM brusatol (used as a control for NRF2 inhibition) for 4 hr before NRF2, FAM129B, p-ERK, and ERK protein levels were detected via immunoblot analysis. (D) NRF2, FAM129B, p-ERK, and ERK protein levels were quantified from immunoblot analyses in (C) (n=3). (E) Cells described in (C) were subjected to indirect immunofluorescence analysis of NRF2 (top) and Hoechst (middle); merged (bottom) panel indicates NRF2 nuclear localization. Additionally, cells from (C) underwent indirect immunofluorescent staining for FAM129B (top) and β-catenin (middle); merged (bottom) panel indicates FAM129B/β-catenin colocalization.