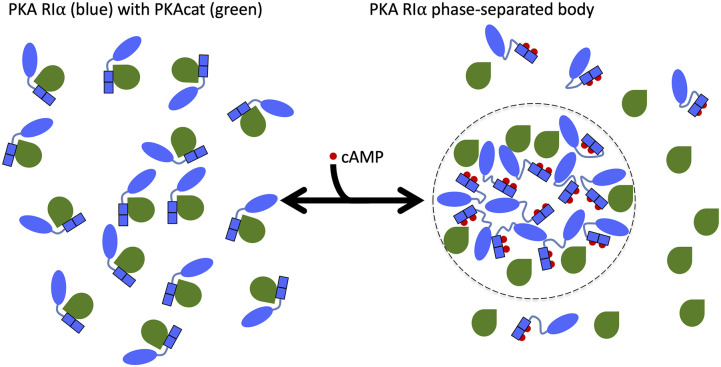
FIG. 1.
Illustration of the regulation of PKA RIα phase separation by different binding partners. Binding of two cAMP molecules (red) per RIα subunit (blue) leads to dissociation (and activation) of PKAcat (green). The increased disorder in the RIα linker region [between the N-terminal dimerization and docking (D/D) domain in oval and tandem cAMP-binding domains in rectangle] and the action of the dissociated PKAcat promote the formation of phase-separated bodies (highlighted on the right with a dotted boundary). In contrast, PKAcat in the absence of cAMP suppresses RIα phase separation by binding to and rigidifying RIα (shown on the left). For clarity, only a half of a holoenzyme, consisting of a single PKAcat subunit and a single RIα subunit, is illustrated.