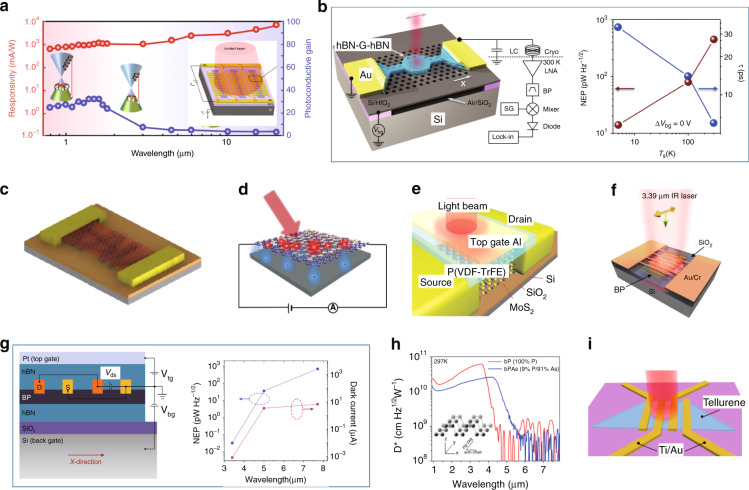
Fig. 6. The surface-illuminated Si/2DM PDs with metal-2DM-metal configuration.
a A wide-band plasmonic enhanced graphene PD and the measured responsivity/photoconductive-gain. b A cavity-coupled graphene bolometer with Johnson noise read-out. Left: the 3D schematic. Right: the NEP and thermal relaxation time of hot electrons as a function of lattice temperature. c A metal-graphene+X-metal configuration PD, for which X is carbon nanotube. d A short-wave infrared graphene PD with a plasmonic enhanced structure on channel. e A ferroelectric polarization gating MoS2 photodetector with an operation wavelength extended to 1.55 μm. f A mid-infrared black-phosphorus PD with a high gain. g A mid-infrared black-phosphorus PD with an operation wavelength extended to 7.7 μm by applying a vertical electric field. Left: the 3D schematic. Right: the NEP and dark current at different wavelengths. h The specific detectivities of the mid-infrared black phosphorus PD and black-PAs-alloy PD as a function of wavelength. i A short-wave infrared tellurene PD. Figures reproduced with permissions from: a ref. 128, ©2018 Springer Nature Limited, under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license (CC BY 4.0, https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/); b ref. 53, ©2018 Springer Nature Limited; c ref. 76, ©2015 Springer Nature Limited, under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license (CC BY 4.0, https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/); d ref. 78, ©2017 American Chemical Society; e ref. 81. ©2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. f ref. 67, ©2016 American Chemical Society; g ref. 29, ©2017 Springer Nature Limited, under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license (CC BY 4.0, https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/); h ref. 129, ©2017 American Chemical Society. i ref. 131, ©2019 American Chemical Society. Further permissions related to the figures should be directed to the copyright holders.