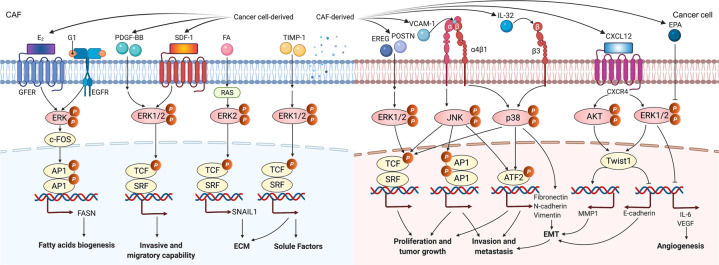
Fig. 4.
MAPK signaling pathway in CAFs and the crosstalk of CAFs with cancer cells. In CAFs, by E2 and G1, the EGFR/ERK signaling upregulated FASN expression for the metabolism of fatty acids. The PDGF-BB and SDF-1 could stimulate the higher invasive and migratory capability of CAFs via ERK1/2 phosphorylation. FA activated RAS upregulating SNAIL1 via ERK2 signaling, which mediated the fibrogenic response of CAFs. TIMP-1 enhanced CAF proliferation and migration and activated ERK1/2 signaling pathway in CAFs by the production of soluble factors. In the crosstalk between CAFs and cancer cells, CAF-derived EREG and POSTN could enhance the cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth by the downstream effector of ERK1/2. VCAM-1 and CAF-derived IL-32 increased the proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and EMT in cancer cells by activating p38/MAPK signaling pathway. Activated CXCL12/CXCR4 signal promoted EMT process through ERK/AKT-Twist1-MMP1 pathway. EPA decreased the expression of IL‑6 and VEGF secretion in CAFs by inhibition of ERK phosphorylation, thereof affecting angiogenesis. E2 17β-estradiol, G1 1-(4-(6-bromobenzo[1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-3a,4,5,9b-tetrahydro-3H-cyclopenta[c]quinolin-8-yl)-ethanone, 1-[(3aS,4R,9bR-rel)-4-(6-bromo-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-3a,4,5,9b-tetrahydro-3H-cyclopenta[c]quinolin-8-yl]-ethanone, PDGF-BB platelet-derived growth factor-BB, FA focal adhesions, TIMP-1 tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1, AP1 activating protein 1, FASN fatty acid synthase, SRF serum response factor, TCF ternary complex factor, POSTN periostin, EPA eicosapentaenoic acid, ECM extracellular matrix, EMT epithelial–mesenchymal transition