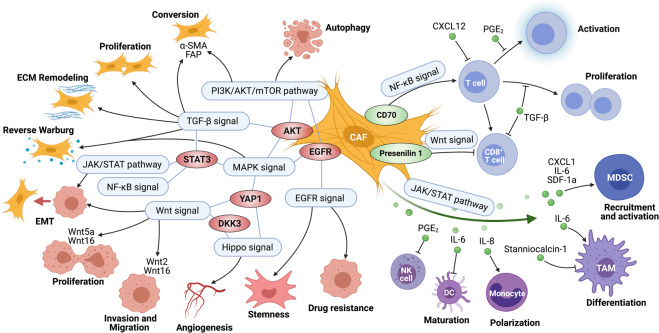
Fig. 5.
Crosstalk of different signaling pathways among CAFs, cancer cells, and immune cells. A reservoir of biological behaviors of CAFs, including CAFs generation, proliferation, ECM remodeling, and energy metabolism, etc. were regulated by several major signals like TGF-β and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways. Importantly, CAF-mediated signaling pathways like JAK/STAT, Wnt, Hippo, MAPK, EGFR, and NF-κB signal were widely involved in cancer cells proliferation, stemness, invasion, migration, metastasis, angiogenesis, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) process, and therapeutic resistance. CAF-mediated signaling pathways did not always display with individual effects, but commonly crossed to each other to form a signaling network in cancer progression by the cross-connections such as STAT3, AKT, and YAP1. As the great source of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors, CAF-secreted factors, including TGF-β1, IL-6, IL-8, CXCL1, CXCL12, and PGE2, etc., affect proliferation and activation of T cell, recruitment and activation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), differentiation, and polarization of monocytes/macrophages, etc. PGE2 prostaglandin E2