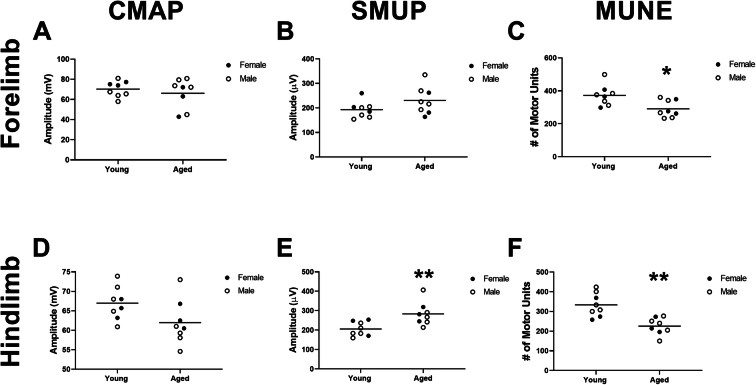
Fig. 5.
Motor unit connectivity is reduced in forelimb and hindlimb muscles of aged rats. In the forelimb, a compound muscle action potential (CMAP) and b single motor unit (SMUP) amplitudes were not significantly altered (p=0.4917 and p=0.1216, respectively), but c motor unit number estimation (MUNE) was significantly lower in aged versus young rats (p=0.0134). In the hindlimb, d CMAP was not significantly altered (p=0.0655), but both e SMUP amplitudes and f MUNE were significantly lower in aged versus young rats (p=0.0074 and p=0.0010, respectively). Young rats, n=8 (3 females, 5 males), and aged rats, n=8 (3 females, 5 males). Unpaired t-test. *p<0.05, **p<0.05