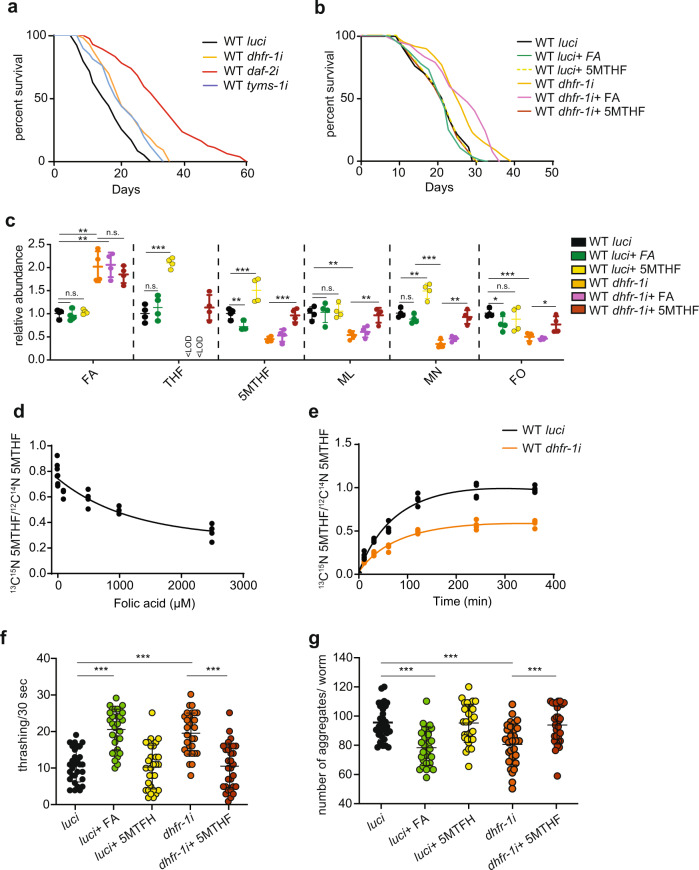
Fig. 2. dhfr-1i prolongs nematode life span in a 5MTHF dependent manner.
adhfr-1 and tyms-1 RNAi treatment increase wild-type life span (from L4 stage). b Supplementation of 10 nM 5MTHF abolishes dhfr-1i longevity (from L4 stage). c Quantitation of folic acid intermediates using targeted mass spectrometry in wild-type worms (day 1) with luci and dhfr-1i treatment in the presence or absence of folic acid and 5MTHF. dhfr-1i increases folic acid and decreases 5MTHF and downstream intermediates. d Increasing concentrations of FA inhibit 13C15N labeled 5MTHF incorporation within a 2 h time period (day 1 adult). e Incorporation of 13C15N labeled 5MTHF over time in worms with luci (black line) and dhfr-1i (orange line) (day 1 adult) each dot represents a single biological replicate. f Thrashing assay of polyQ35 worms (day 7 adult). g Protein aggregate quantitation in polyQ40 model (day 7 adult). dhfr-1i or FA supplementation are beneficial, whereas 5MTHF is detrimental for motility and aggregate accumulation. Each dot represents a single worm. a, b n = 150 worms per repeat per condition, N = 3 biological replicates. c N = 5 biological replicates. d, e N = 4 independent biological replicates. f, g n = 30 worms, N = 3 independent biological replicates, only one biological replicate is shown. a, b Statistics were performed with the two-sided Mantel–Cox log-rank test (Supplementary Table 7 for statistics). c, f, g Significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. *p < 0.5, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (Supplementary Table 8 for statistics).