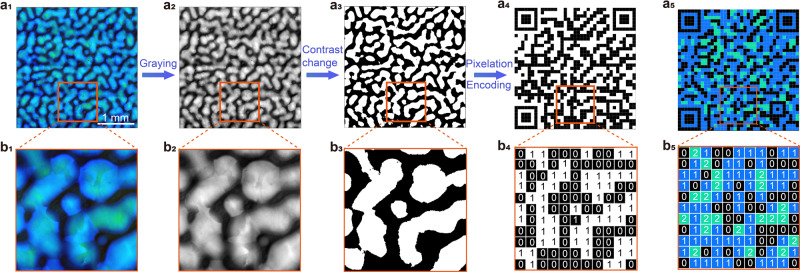
Fig. 5. Binary anti-faking QR codes.
a1 POM image of PS-BPLCs at Stage IV with low magnification. a2 The image obtained after the gray-level conversion of a1. a3 An image of the binarization of a2. a4 The binary codes obtained from a3 after pixelation and encoding processes. a5 Large-scale ternary QR code with a pixel resolution of 37 × 37 encoded from a1 undergoing ternary and pixelation processes. b1–b3 The magnified image of the orange squared area in a1–a3. b4–b5 The binary and ternary codes of the orange-squared area in a4, a5. In binary codes, the “black” or “white” pixel represents “0” or “1”. In ternary codes, the “green”, “blue”, or “black” pixels in a5, b5 represents “2”, “1”, or “0”.