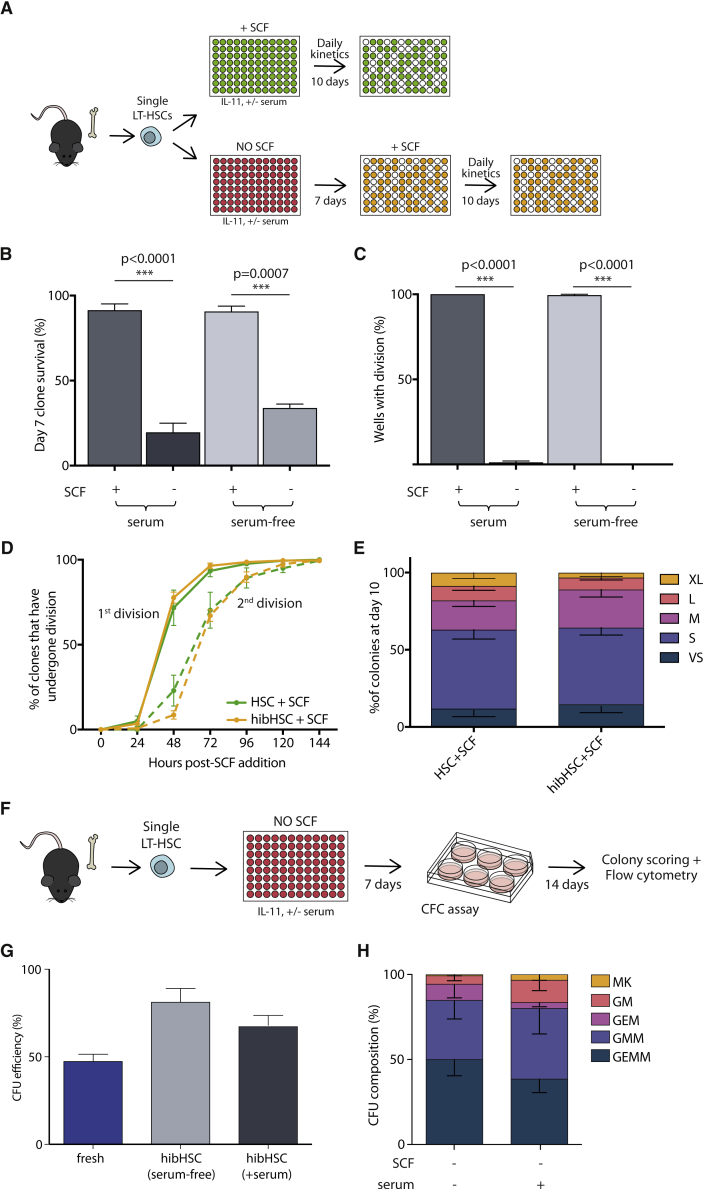
Figure 1.
Absence of SCF and TPO maintains HSCs as single multi-potent cells in vitro
(A) Single CD45+EPCR+CD48−CD150+Sca1high LT-HSCs were sorted into individual wells and cultured in the presence of IL-11, in serum-supplemented or serum-free medium and in the presence or absence of SCF. For SCF-supplemented cultures (green plate), daily cell counts were performed for 10 days. For cultures only containing IL-11 (red plate), HSCs were supplied with SCF on day 7 post-isolation after which daily cell counts were performed for an additional 10 days. In all cases, clone size was assessed at day 10 post-SCF addition.
(B) HSC survival is decreased in the absence of SCF compared with SCF-supplemented medium (+serum/+SCF n = 355, 5 biological replicates; +serum/−SCF n = 1,722, 7 independent experiments; −serum/+SCF, N = 144, 2 independent experiments, −serum/−SCF n = 284, 3 independent experiments).
(C) Numbers of wells with >2 cells were scored to determine the number of clones that had divided. At day 7 post-isolation, only culture conditions without SCF maintained HSCs as single cells.
(D) Cell division kinetics post-SCF addition. Entry into cell cycle was comparable between freshly isolated HSCs (green solid line) and cells that had been maintained as single cells for 7 days (orange solid line) in serum-supplemented media. Time to subsequent cell division (dotted lines) was not significantly different between conditions (SCF added at day 0, n = 355, 5 independent experiments; SCF added at day 7, n = 1,722, 7 independent experiments).
(E) Colony size was measured on day 10 post-SCF addition and no difference in clone size distribution was observed between HSCs cultured in the presence of SCF from day 0 and post-hibernation HSCs (day 7 + 10).
(F) Single LT-HSCs were cultured for 7 days in IL-11 alone, in serum-supplemented or serum-free medium. After 7 days, single hibernating LT-HSCs were individually transferred into a cytokine-rich methylcellulose CFC assay and cultured for an additional 14 days. On day 14, lineage composition of individual colonies was assessed by flow cytometry.
(G) Colony-forming efficiency for freshly isolated single LT-HSCs, single LT-HSCs cultured in serum-supplemented and serum-free hibernating cultures (fresh, n = 300, 3 biological replicates; serum-free, n = 121, 5 independent experiments; +serum, n = 230, 6 independent experiments).
(H) Colony subtype analysis showed that the majority of single cells (~80%) generated colonies of at least three lineages in colony-forming unit (CFU) assays (hibHSC serum-free, n = 70, 4 independent experiments; hibHSC + serum, n = 166, 3 independent experiments). Colonies were defined as MK (containing cells positive for megakaryocyte marker CD41), GM (containing cells positive for granulocyte/monocyte markers Gr1 and CD11b), GEM (positive for GM and erythrocyte markers Gr1, CD11b, and Ter-119), GMM (positive for GM and MK markers), and GEMM (positive for GM, MK, and E markers), as described in the Experimental procedures. Bars show mean with SEM. Unpaired t test: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.