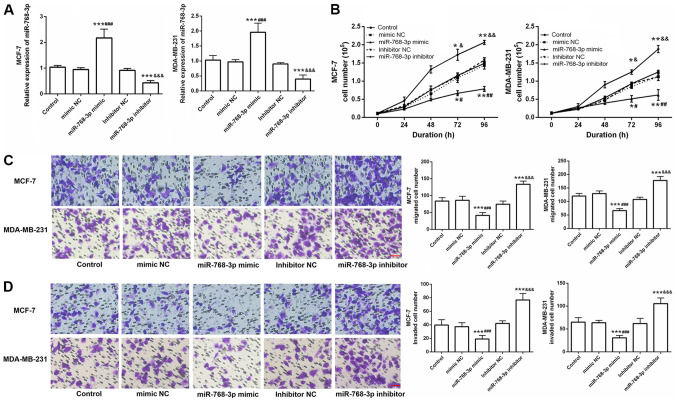
Figure 3.
Effects of miR-768-3p on the function of breast cancer cells in vitro. (A) Expression level of miR-768-3p in cells after transfection with the miR-768-3p mimic or inhibitor and corresponding controls using RT-qPCR. The results confirmed that the miR-768-3p mimic and inhibitor had a higher transfection efficiency in cancer cells compared with the control, mimic NC and inhibitor NC groups, respectively (***P<0.001, compared with control; ###P<0.001, compared with mimic NC; &&&P<0.001 compared with inhibitor NC). (B) Viability ability was examined. Compared with the control group, the miR-768-3p mimic group significantly inhibited cell viability, while the miR-768-3p inhibitor group significantly promoted cell viability (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, compared with control; #P<0.05, ##P<0.001, compared with mimic NC; &P<0.05, &&P<0.001, compared with inhibitor NC). (C) Representative images and quantitative analysis of cell migration by transwell assays. (D) Representative images and quantitative analysis of cell invasion by transwell assays. Compared with the control group, the miR-768-3p mimic group significantly promoted cell migration and invasion, while the miR-768-3p inhibitor group significantly promoted cell migration and invasion. The randomly chosen fields were photographed (magnification, ×200) (***P<0.001, compared with control; ###P<0.001, compared with mimic NC; &&&P<0.001, compared with inhibitor NC) (scale bar=200 µm). miR, microRNA; RT-q, reverse transcription-quantitative; NC, negative control; control, untransfected cells.