Figure 1. More Than Meets the Eye with the TCA Cycle.
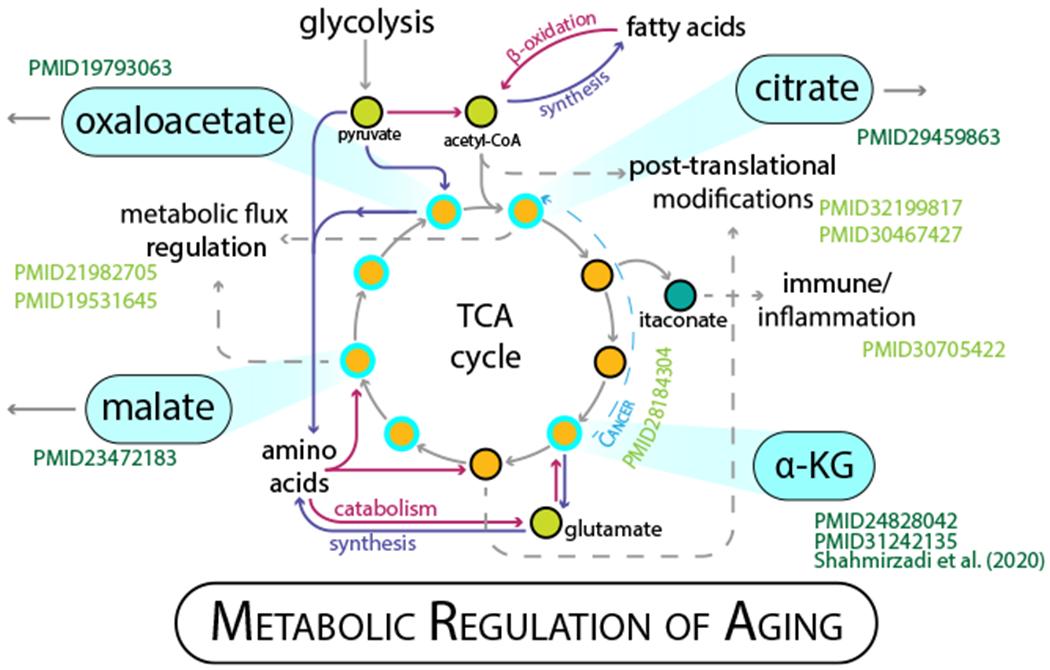
The TCA cycle is a metabolic hub, processing inputs from glucose, fatty acid, and amino acid catabolism; generating reducing equivalents for the respiratory chain; and providing precursors for biosynthesis. What happens in the mitochondria influences cell function in different cellular compartments, including diverse regulatory mechanisms (allostery, post-translational modification, epigenetic regulation of gene expression) and diverse cellular processes (immune and inflammatory pathways, and growth regulation). The main inputs are depicted as circles in neon green, with canonical pathways and functions highlighted by solid arrows and main TCA intermediates in orange. A few of the many signaling roles that metabolites of the TCA participate in are indicated by dashed arrows. Metabolites that have been linked specifically to longevity are highlighted by cyan outlines. Key players including alpha-ketoglutarate, the subject of Asadi Shahmirzadi et al. (2020), are shown in the cyan flyouts. Aging references shown in dark green.
