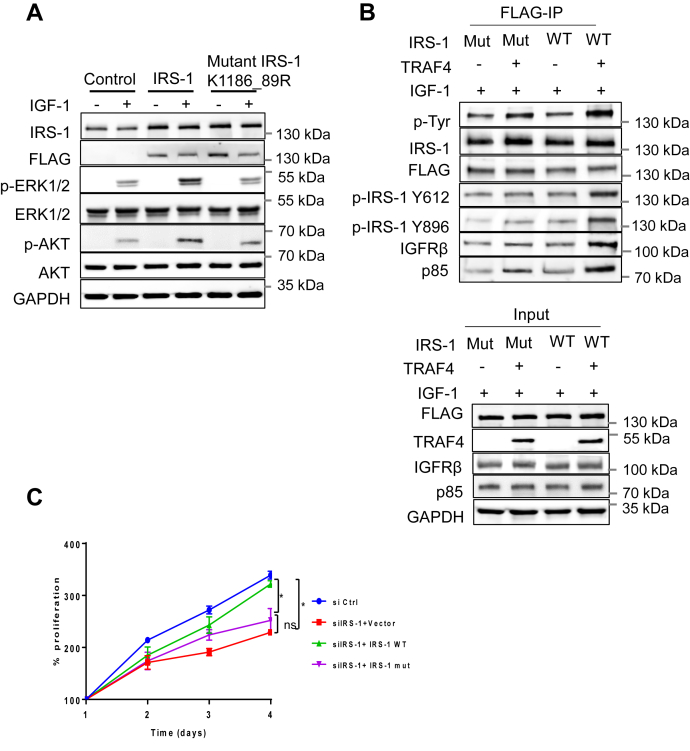
Figure 5.
Mutation of TRAF4-targeted IRS-1 ubiquitination sites inhibits IGF-1 signaling and TRAF4-promoted IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation.A, IRS-1 ubiquitination mutant failed to induce downstream ERK and AKT phosphorylation upon IGF-1 stimulation. MCF-7 cells were transfected either with control vector, FLAG-IRS-1 WT or mutant IRS-1 (K1186_1189R). MCF-7 cells were then serum starved for 24 h and treated with or without IGF-1 (100 ng/ml) for 15 min. Western blot was performed to determine the level of ERK and AKT phosphorylation. B, mutation of K1186 and K1189 of IRS-1 inhibits TRAF4-promoted IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation and its interaction with IGFR. 293T cells were cotransfected with FLAG-tagged wildtype or mutant IRS-1 in the absence or presence of TRAF4. The cells were then serum starved for 24 h and treated with IGF-1 (100 ng/ml) for 15 min. The wildtype or mutant IRS-1 was then immunoprecipitated using an anti-FLAG antibody. Western blot was then performed to determine IRS-1 phosphorylation level and its interaction with IGFR (top). Overexpression of TRAF4, IRS-1 WT, and mutant was determined by Western blot. GAPDH was used as an internal control (bottom). C, IRS-1 wildtype but not the ubiquitination mutant rescued the effect of siIRS-1 on cell proliferation. Shown is a cell proliferation assay in MCF-7 cells after IRS-1 knockdown and transfection with either WT IRS-1 or IRS-1 mutant. ∗p < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Data are presented as mean ± SD.