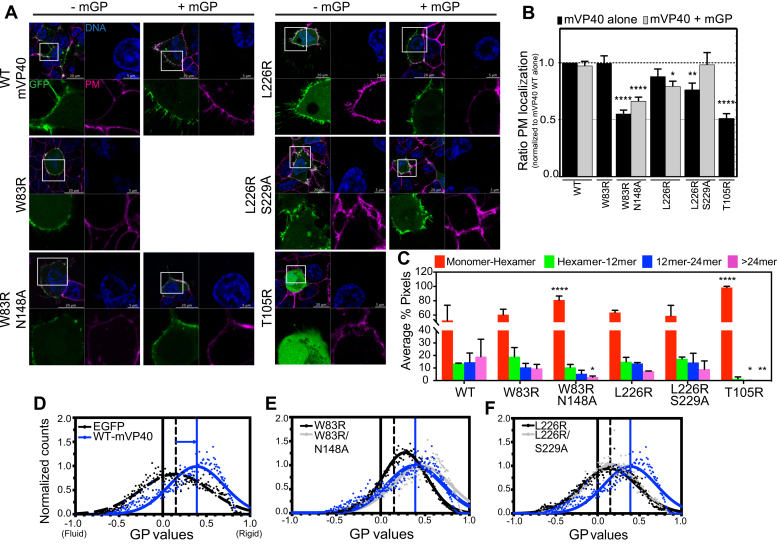
Figure 2.
N-terminal domain and C-terminal domain oligomerization interfaces required for efficient mVP40 trafficking and oligomerization at the plasma membrane.A, confocal live images of cells expressing EGFP constructs (green) +/− glycoprotein mGP, stained for DNA (blue) and plasma membrane (PM, pink). B, ratio of PM retention from A quantified by calculating the integrated density of pixels at PM to total pixels within the cell and normalized to WT. C, average % pixels with each estimated oligomerization form from number and brightness analysis performed 24 h.p.t of HEK293 cells with EGFP-mVP40 constructs. Functional budding assays were performed to assess the capacity of WT-mVP40 and mutants to produce virus-like particles. Experimental and fitted normalized generalized polarization (GP) distribution curves of Laurdan dye across PM of HEK293 cells with EGFP (black dashed line) (D), mVP40 mutants of N-terminal domain (E), and C-terminal domain (F) oligomerization interfaces, compared with WT (blue line). GP values range from −1 (very fluid lipid domains) to +1 (very rigid lipid domains). The fitting procedure was performed using a nonlinear Gaussian curve. Values are reported as mean ± SEM (B) or SD (C) of three independent means. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons were performed (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.0005, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).