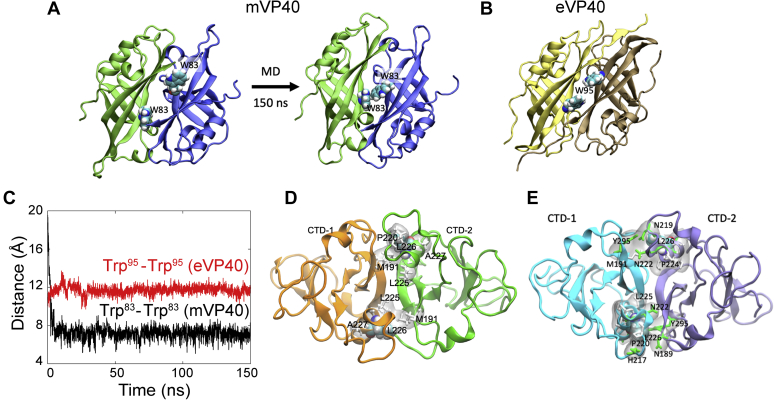
Figure 8.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of the oligomer interfaces ofmVP40.A, the mVP40 oligomer interface modeled based on eVP40 structure initially shows separated W83 residues as in eVP40 (Trp95) shown in (B). However, upon 150 ns MD simulation, the structure relaxes so that the interface residues W83 interact with each other. C, center of mass distance between Trp83 residues in mVP40 (black curve) and between Trp95 residues in eVP40 (red curve) as a function of time. D, dimer–dimer interface in the mVP40 filament (CTD from each monomer is shown in different colors). The hydrophobic residues within 3 Å of Leu226 at the mVP40 dimer–dimer interface are highlighted. The hydrophobic interaction at the dimer–dimer interface may provide an agile interface, giving flexibility to the filaments. E, zoom into dimer–dimer interface in the mVP40 filament formed through CTD–CTD linear oligomerization as proposed by Wan et al. (31). (CTD from each monomer is shown in different colors). CTD, C-terminal domain.