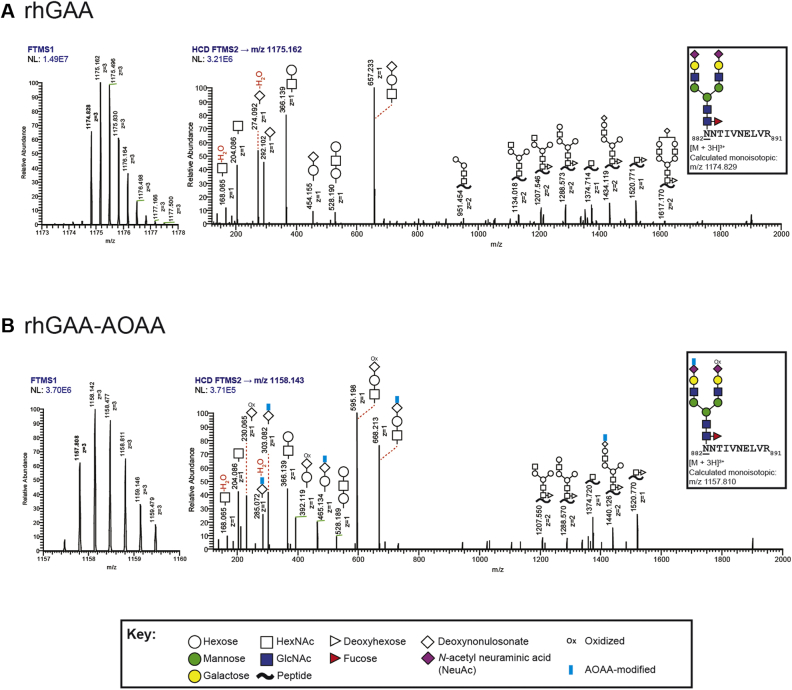
Figure 2.
Glycopeptide analysis of rhGAA and rhGAA–AOAA by MS. Unmodified and modified rhGAAs were subjected to trypsinization followed by glycopeptide analysis by LC-MS. Representative precursor MS1 and HCD MS2 spectra of the rhGAA tryptic glycopeptide, 882NNTIVNELVR891, bearing the highly abundant glycan structure FA2G2S2 at Asn882 (underlined), are shown for unmodified (A) and AOAA-modified (B) rhGAA. Glycan annotations are represented by symbols according to SNFG conventions. Glycan oxonium ions are annotated in the region 150 to 800 m/z. Fragment ions consistent with various glycosidic bond cleavages of the glycan attached to the peptide are also annotated. Calculated monoisotopic m/z values are displayed, and the observed monoisotopic m/z values are bolded in the MS1 spectra. [FTMS (Orbitrap); HCD; NL; m/z]. A, the MS1 and HCD MS2 spectra are consistent with the glycan structure FA2G2S2, with oxonium ions 292 and 274 m/z indicative of a glycan species containing sialic acid. B, HCD MS2 spectra for FA2G2S2 in rhGAA–AOAA contains fragments consistent with only one of the two oxidized sialic acids further derivatized with AOAA (FA2G2S2, NeuAcAOAA+NeuAcOxi). Unique oxonium ions were detected that are consistent with the oxidation of sialic acids (230 and 392 m/z) or the modification of sialic acids with AOAA (285, 303, 465, and 668 m/z). AOAA, aminooxyacetic acid; FTMS, Fourier transform mass spectrometry; GAA, acid alpha-glucosidase; HCD, higher-energy collision dissociation; HCD MS2, higher-energy collisional dissociation MS2; NL, normalization level, signal intensity of base peak; rhGAA, recombinant human GAA; SNFG, Symbol Nomenclature for Glycans.