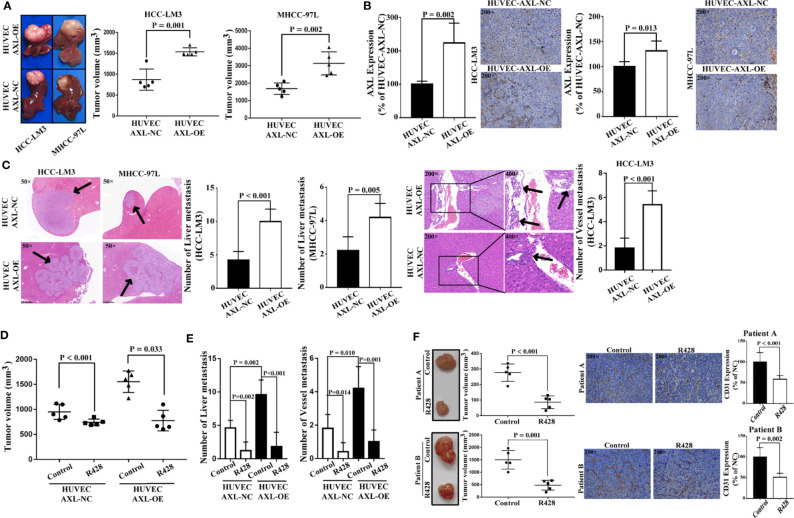
Figure 7.
HUVECs overexpressing AXL promote tumor growth and metastasis of HCC in vivo. (A) HUVECs overexpressing AXL promoted tumor growth in vivo (HCC-LM3: p = 0.001; MHCC-97L: p = 0.002). (B) AXL was highly expressed in the vessels of the HUVEC-AXL-OE group compared with the HUVEC-AXL-NC group (HCC-LM3: p = 0.002; MHCC-97L: p = 0.013). (C) HUVECs overexpressing AXL promoted vessel metastasis and liver metastasis of HCC-LM3 cells in vivo, and HUVECs overexpressing AXL, but not HUVEC-AXL-NC cells, induced liver metastasis and vessel metastasis of MHCC-97L cells in vivo. (D) R428 treatment decreased tumor volume induced by HUVECs overexpressing AXL and HCC-LM3 cells or MHCC-97L cells. (E) R428 treatment decreased vessel metastasis and MVI of HCC induced by HUVECs overexpressing AXL and HCC-LM3 cells or MHCC-97L cells. (F) R428 treatment decreased tumor volume in the HCC PDX models (patient A: p < 0.001; patient B: p = 0.001). Furthermore, in the HCC PDX models, CD31 expression in the tumors of mice treated with R428 was lower compared with that in the tumors of mice treated with the control (patient A: p < 0.001; patient B: p = 0.002).