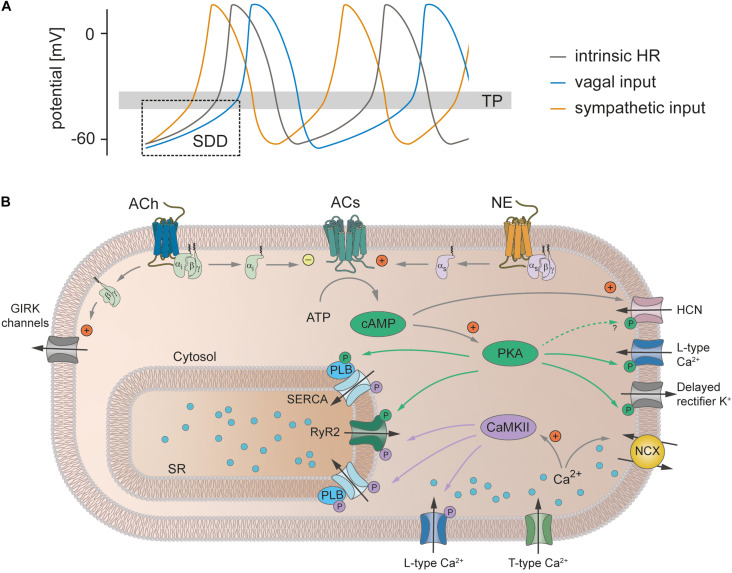
FIGURE 3.
Heart rate regulation by the autonomic nervous system. (A) SAN cell action potentials. The intrinsic action potential rate is depicted in gray. Activity of the sympathetic nervous system (orange) leads to a steeper SDD, decreases the time to reach the threshold potential (TP) for the next action potential thereby increasing action potential frequency and consequently also heart rate (positive chronotropic effect). Vagal input flattens SDD, lowers the maximum diastolic potential and thereby increases the time to reach the TP. Action potential frequency and hence HR decrease (negative chronotropic effect). (B) Signaling cascades underlying the chronotropic effect. Release of norepinephrine (NE) from sympathetic nerve terminals leads to activation of Gs protein-coupled β-receptors. Subsequent stimulation of adenylyl cyclases (ACs) increases the cytoplasmic concentration of cAMP. cAMP directly facilitates the opening of HCN channels and activates PKA, which in turn phosphorylates various proteins (indicated by green arrows and green circles), thereby increasing their activity. In addition, sympathetic activity increases the intracellular Ca2+ concentration, which increases the activity of NCX and CaMKII. This in turn phosphorylates various target proteins (indicated by purple arrows and circles). Taken together, this steepens the SDD, increases the repolarization rate and thereby increases the action potential frequency (see text for further details). In contrast, the release of acetylcholine (ACh) during vagal activity leads to the activation of Gi protein-coupled M-receptors. ACs are inhibited by the Gi protein and thus the opposite effect of sympathetic activation unfolds. In addition, the β/γ-subunit activates GIRK channels that make the maximum diastolic potential more negative. Abbreviations: ACh, acetylcholine; ACs, adenylyl cyclases; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CaMKII, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; GIRK, G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels; HCN, hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel; NE, norepinephrine; PKA, protein kinase A; PLB, phospholamban; RyR2, ryanodine receptor 2; SERCA, sarco-/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase; SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum.