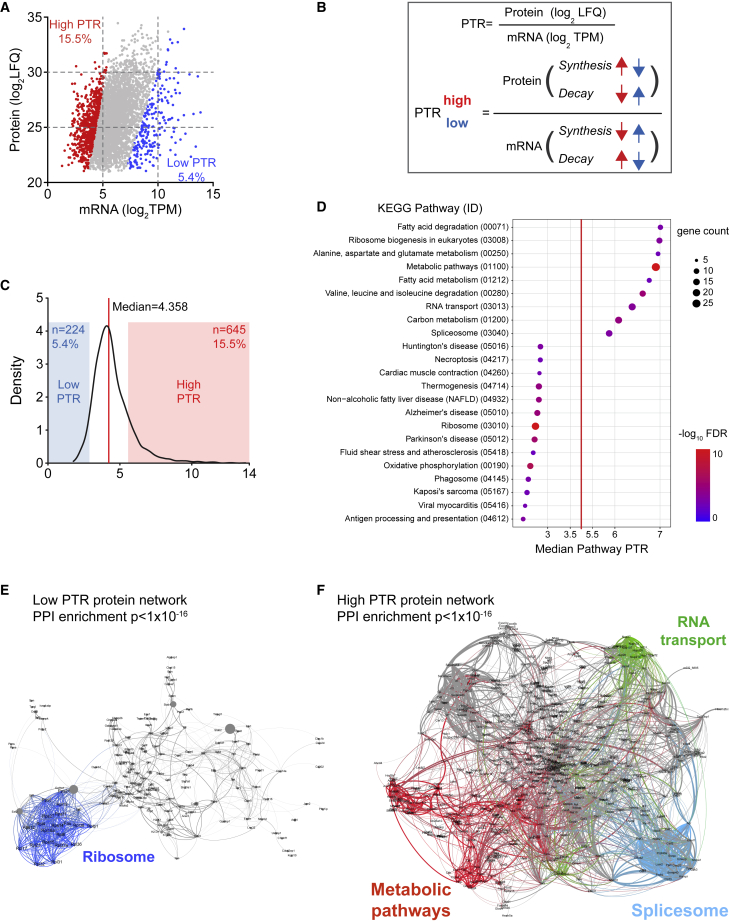
Figure 3.
Post-transcriptional regulation of the protein abundance
(A) Scatterplot of protein and RNA abundance (mean expression across all zones). Red and blue mark the genes with a high and low PTR as defined in (B and C).
(B) Protein-to-transcript ratio (PTR) definition. Regulation on synthesis/decay, which contributes toward high or low PTR are indicated with arrows marked with blue and red, respectively.
(C) Distribution of PTR values of protein-RNA pairs. The red line indicates the median and the red and blue overlay display ±1 SD from the median, defined as high or low PTR range.
(D) Dot plot of the KEGG pathways significantly enriched in the gene sets corresponding to low or high PTR. Pathways (y axis) are ordered from low to high PTR by increasing median PTR value (x axis) of the proteins enriched in the pathway. Dot size and color indicate gene count and −log10 FDR for each pathway, respectively.
(E and F) Interaction network of low (E) and high (F) PTR proteins. Interaction was based on STRING and visualized by Gephi. Node size is proportional to the protein abundance (LFQ) and the edge weight is proportional to the combined interaction score. Proteins (node) and the related interaction (edge) belonging to selected pathways were highlighted as indicated in the figures.