Figure 2.
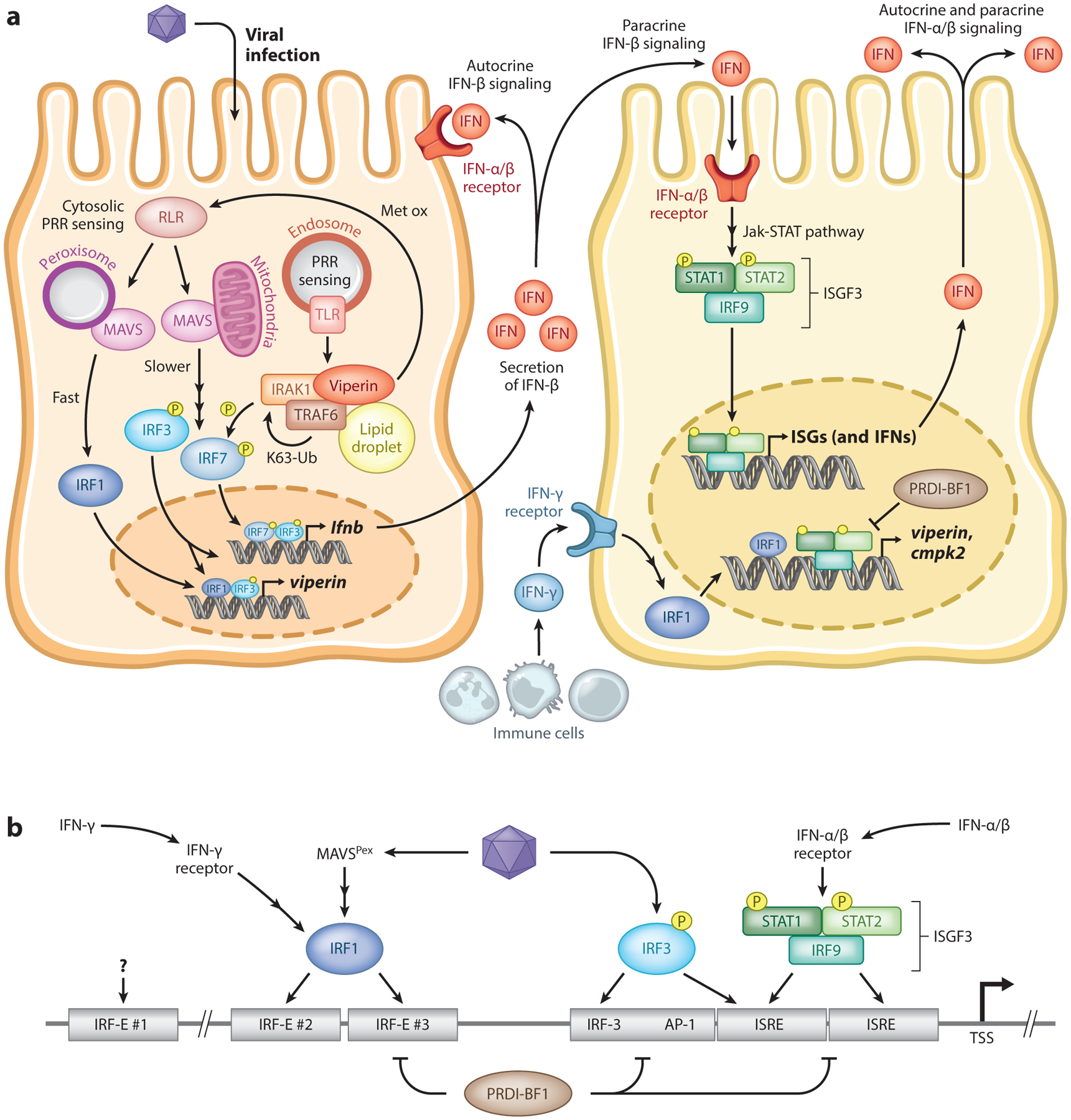
IFN-dependent and -independent pathways leading to induction of viperin upon viral infection. (a) Upon viral infection, sensing of viral nucleic acids by PRRs leads to the activation of downstream signaling factors that result in the induction of IFNs and, in some cases, viperin. The induction of IFN-β can occur to one of several mechanisms, including those dependent on endosomal TLRs and mitochondrial MAVS, that culminate in the activation of the transcription factors IRF3 and IRF7 that bind to the IFNB promoter and induce its expression. The direct induction of viperin can occur through peroxisomal MAVS and downstream activation of IRF1 or by IRF3. Viperin itself can increase IFNB induction by promoting TRAF6-dependent ubiquitination of IRAK1 and phosphorylation of IRF7. IFN-β is secreted and signals both in autocrine and paracrine manners upon binding to its receptor. Downstream activation of the Jak-STAT pathway results in the formation of the heterotrimeric complex ISGF3, which translocates to the nucleus and binds to the promoter of ISGs, including that of viperin, and other IFNs. The transcription factor PRDI-BF1 can act as a negative regulator by competing with ISGF3 for promoter binding. Additionally, IFN-γ secreted primarily by immune cells can activate IRF1 and directly induce viperin expression. (b) In binding of transcription factors to the VIPERIN promoter, the promoter contains two adjacent ISRE sites immediately upstream of the TSS for ISGF3 complex binding. The transcription factor IRF3 can directly bind to the ISREs and also to an upstream sequence. Activation of IRF1 by either IFN-γ signaling or peroxisomal MAVS can bind to two IRF-binding elements, IRF-E #2 and #3. A further upstream IRF-E sequence exists but does not appear to be involved in IRF1 binding. Abbreviations: AP-1, activator protein 1; IFN, interferon; IRAK1, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; IRF-E, interferon regulatory factor element; ISGF3, interferon-stimulated gene factor 3; ISRE, interferon-stimulated response element; Jak-STAT, Janus kinase signal transducer and activator of transcription protein; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral signaling; P, phosphorylated; PRDI-BF1, positive regulatory domain I binding factor 1; PRR, pattern recognition receptor; RLR, retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptor; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription protein; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor–associated factor 6; TSS, transcription start site.
