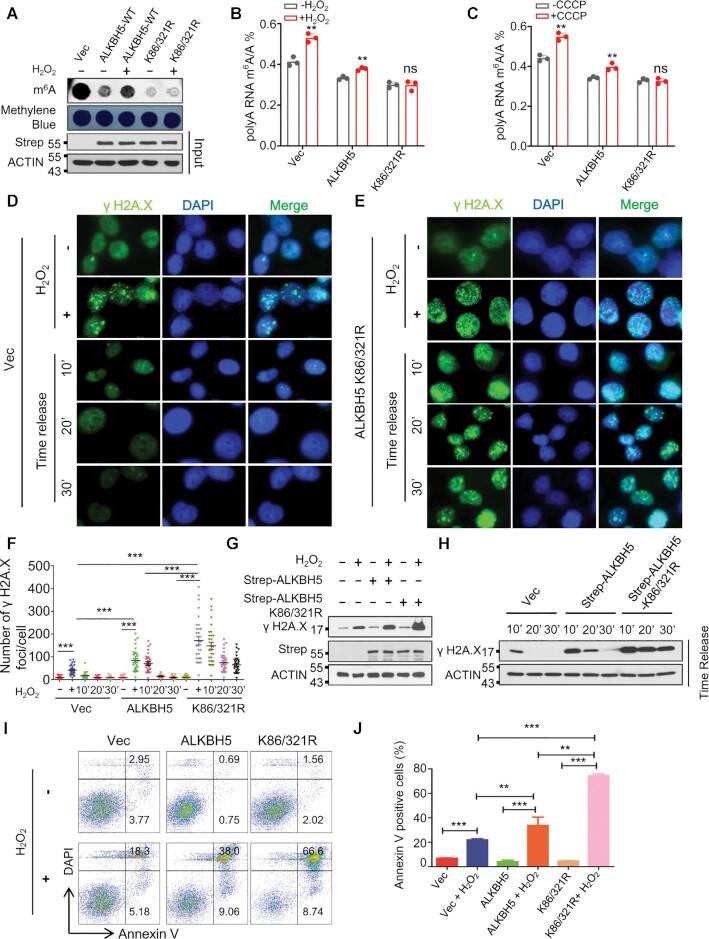
Figure 3.
ALKBH5 SUMOylation is mainly responsible for ROS-induced global increase in mRNA m6A methylation. (A) Dot-blot assay showing that SUMOylation-deficient mutant ALKBH5 overexpression completely blocks ROS-induced global increase in mRNA m6A methylation. Strep tagged wild-type or SD-mutant ALKBH5 was transfected into HEK293T cells. Half of cells were used for western blot analysis to confirm the expressions of ectopically expressed plasmids, and the rest of cells were used for dot-blot analysis. (B, C) LC–MS/MS analyses indicating ROS induces global mRNA m6A methylation via ALKBH5 SUMOylation. HEK293T cells stably expressing vector, wild-type, or SUMOylation-deficient mutant ALKBH5 were treated with or without H2O2 (B) or CCCP (C) for 6 h, and subjected to LC–MS/MS analysis of mRNA m6A methylation. (D, E) γ H2A.X immunostaining analysis showing that SUMOylation-deficient mutant ALKBH5 overexpression dramatically delays H2O2–induced DNA damage repair. HeLa cells stably expressing Vec (D), or ALKBH5 K86/321R (E) were treated with H2O2, which was removed after 6 h. γ H2A.X immunostaining analyses were performed at time intervals between 10 and 30 min. (F) γ H2A.X foci quantitative data for D, E and Supplementary Figure S17. (G, H) Western blot analysis showing that SUMOylation-deficient mutant ALKBH5 overexpression significantly inhibits H2O2–induced DNA damage repair. (I) Cell apoptosis analyses showing ALKBH5 K86/321R overexpression markedly increases ROS-induced cell apoptosis. Apoptosis analyses were performed in HEK293T cells transfected with Strep tagged vector, or vectors expressing ALKBH5 or Strep tagged ALKBH5 K86/321R in the presence or absence of H2O2. (J) Histograms showing the summary and statistical analysis of Figure 3I.