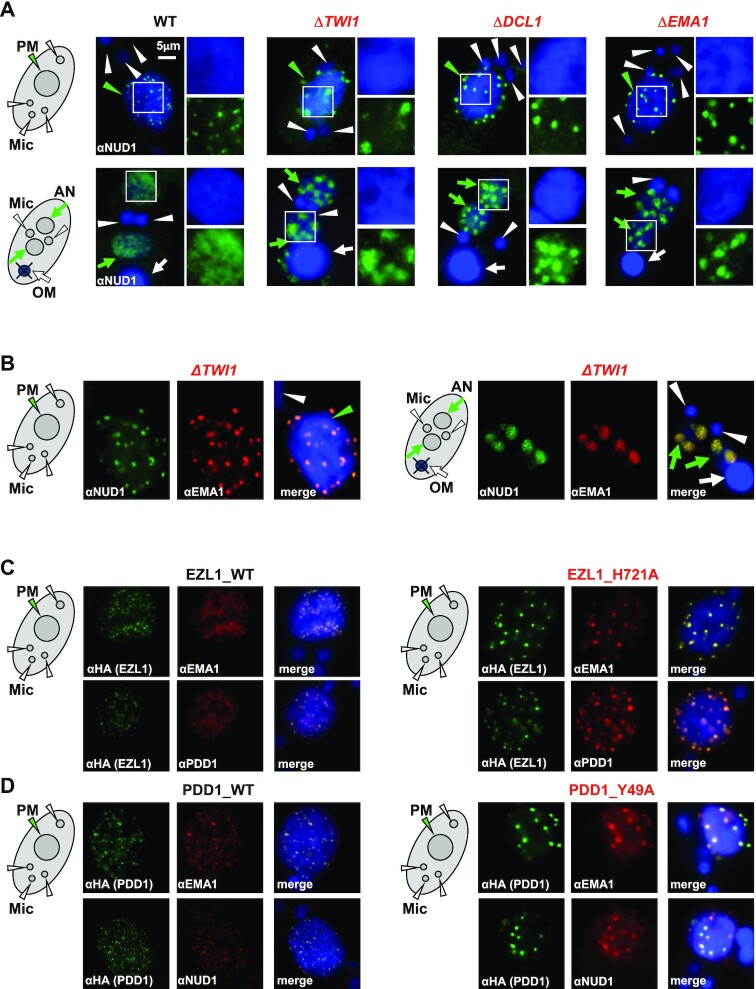
Figure 5.
Nuclear RNAi and histone methylation-binding drive dispersion of Polycomb bodies. (A) RNAi-dependent localization of the EZL1 complex. WT and the designated RNAi mutants at early (top panels: 6 h post-mixing) and late conjugation (bottom panels: 10 h post-mixing) were stained with the anti-NUD1 antibody (green) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Parental MAC (PM): green arrowhead; developing MAC (AN): green arrows; MIC (Mic): white arrowheads; old MAC (OM): white arrow. Granularity analysis of the EZL1 complex foci in the images was provided in Supplemental Figure S11C. (B) Co-localization of the EZL1 complex and EMA1 in ΔTWI1 cells. Cells at early (left panels: 6 h post-mixing) and late conjugation (right panels: 10 h post-mixing) were co-stained with the anti-NUD1 (green) and anti-EMA1 (red) antibodies; counterstained with DAPI (blue). Note their abnormal aggregation at the nuclear periphery or DAPI-poor regions. (C) Co-localization of the EZL1 complex, EMA1, and PDD1 in WT and EZL1 H721A cells (methyltransferase dead). EZL1-HA WT and EZL1-HA H721A cells were co-stained with the anti-HA (green) and anti-EMA1 antibodies (red; top panels), or the anti-HA (green) and anti-PDD1 antibodies (red; bottom panels); counterstained with DAPI (blue). Note abnormal aggregation in EZL1 H721A cells. (D) Co-localization of the EZL1 complex, EMA1 and PDD1 in WT and PDD1 Y49A cells (methyl-binding deficient). PDD1-HA WT and PDD1-HA Y49A cells were co-stained with the anti-HA (green) and anti-EMA1 antibodies (red; top panels), or the anti-HA (green) and anti-NUD1 antibodies (red; bottom panels); counterstained with DAPI (blue). Note abnormal aggregation in PDD1 Y49A cells.