Figure 2.
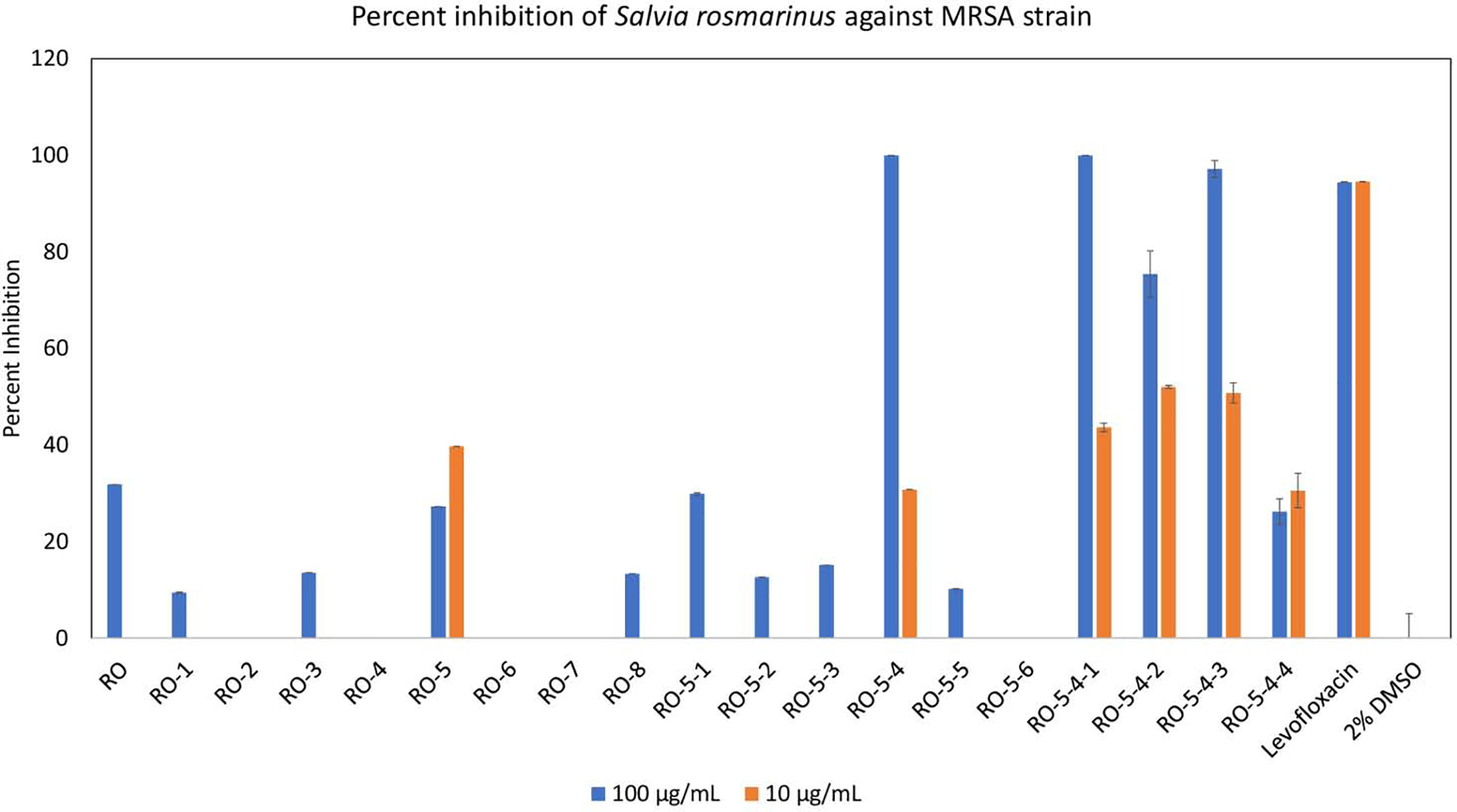
Percent inhibition of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strain AH1263 growth by Rosmarinus officinalis methanol extract (RO) and fractions therefrom. The fractionation scheme can be seen in Figure S1. The initial extract (RO) exhibited partial inhibition at high concentration (100 μg/mL) but no inhibition at low concentration (10 μg/mL). Fractionation of the initial extract (RO) yielded eight fractions (RO-1 through RO-8), of which one fraction (RO-5) possessed strong antimicrobial activity. Fraction RO-5 was subsequently fractionated into six sub-fractions (RO-5–1 through RO-5–6), of which RO-5–4 was active. Fraction RO-5–4 was separated into four sub-fractions, RO-5–4-1 through RO-5–4-4, all of which exhibited significantly high inhibitions of MRSA growth at 100 μg/mL. Mean percent inhibition was calculated from triplicate assays wells and error bars represent standard error of the triplicates. The known antimicrobial agent levofloxacin served as positive control, and vehicle (2% DMSO) served as negative control.
