Figure 5.
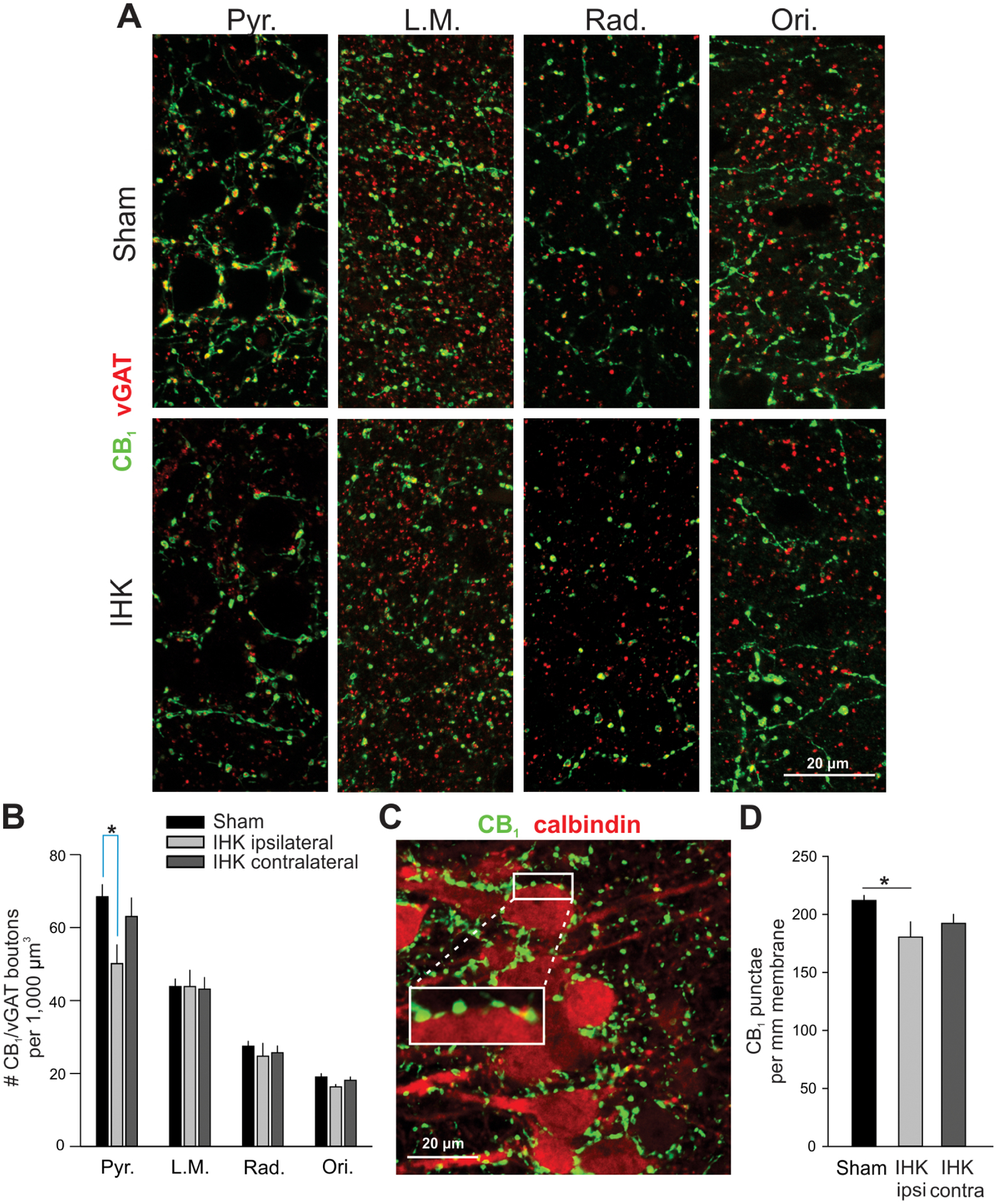
Reduced perisomatic innervation of CA1 PCs by CCK+ interneurons in IHK mice. (A) Representative confocal images showing immunostaining of CB1 and vGAT in ipsilateral ventral hippocampi of sham control and IHK mice. (B) Summary of the number of axon terminals double immunopositive for CB1/vGAT in all CA1 layers; 36–38, 14–15, and 14–16 resected hippocampal slices were used for sham control, IHK (ipsilateral), and IHK (contralateral) hippocampi, respectively, from 10 sham control and 8 IHK mice. Pyr., stratum pyramidale; L.M., stratum lacunosum moleculare; Rad, stratum radiatum; Ori, stratum oriens. (C) A representative Z-stack projection image of CA1 stratum pyramidale in the ventral ipsilateral hippocampus from a sham control mouse showing immunostaining of CB1 (green) and calbindin (red). CB1+ boutons were closely juxtaposed on the surface of somata of calbindin+ CA1 PCs. The area of white rectangle was magnified to show juxtapositions of CB1+ boutons along the surface of CA1 PCs. (D) Summary of the number of CB1+ axon terminals per mm membrane of CA1 PCs. The numbers of CB1+ punctae were normalized by perimeters of CA1 PCs for comparisons. The mean of the numbers of CB1+ terminals within each resected hippocampal slice was used to determine whether there was a difference in the number of CB1+ terminals among sham controls (n = 44), IHK ipsilateral (n = 16), and IHK contralateral (n = 20). * indicates p < 0.05.
