Figure 4. Fxr signaling in Paneth cells is essential for Western diet (WD)-mediated Paneth cell defects.
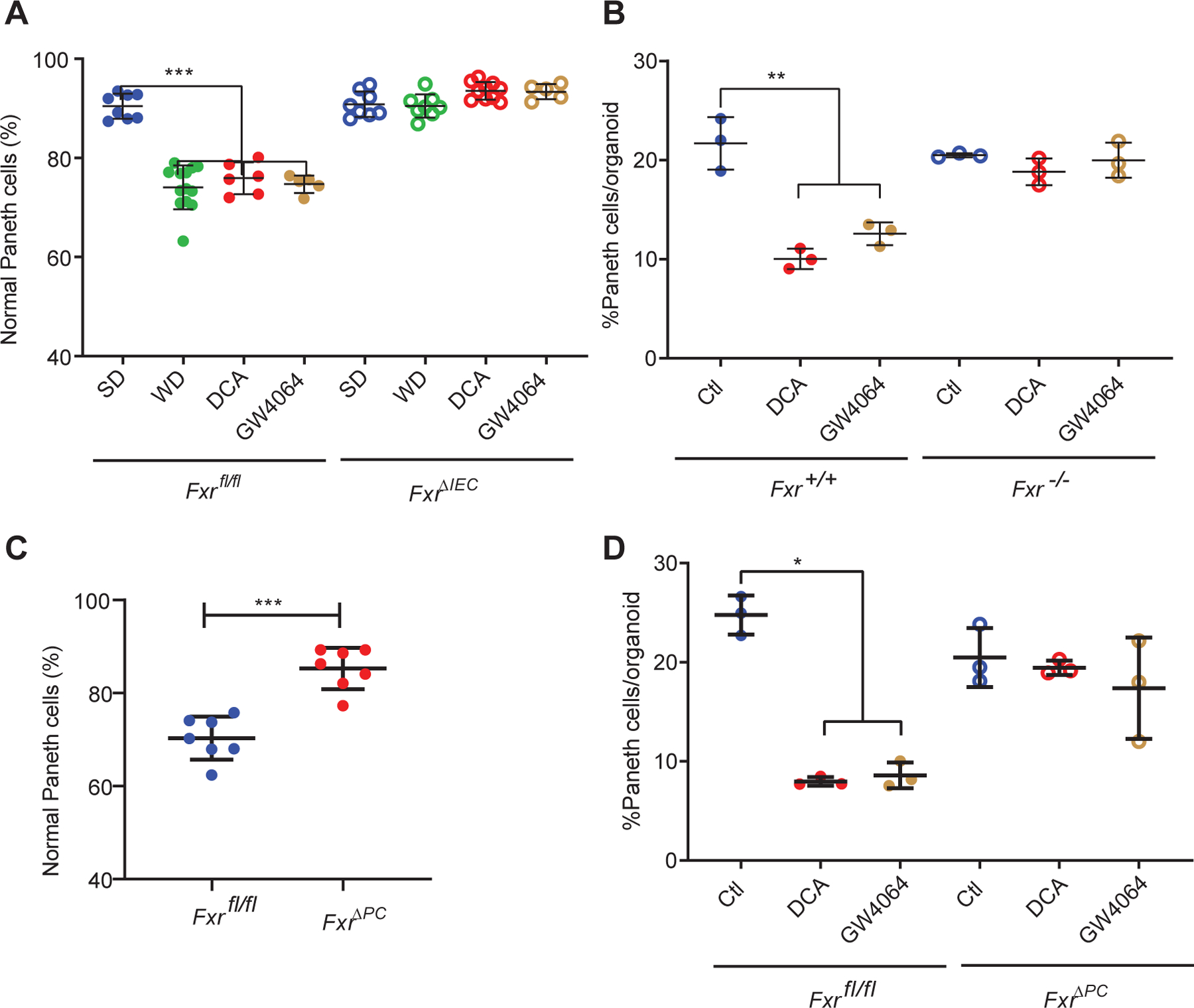
(A) WD, DCA, and GW4064 triggered Paneth cell defects in Fxrfl/fl mice, but the effects were abrogated in the FxrΔIEC mice (P=0.0005). Total n=5~13/group. (B) Ileal organoids derived from Fxr−/− and Fxr+/+ mice showed differential responses to DCA and GW4064. Whereas DCA and GW4064 both reduced the percentages of Paneth cells/organoid in the Fxr+/+ organoids, such an effect was abrogated in the Fxr−/− organoids (P=0.0036). (C) WD-mediated Paneth cell defects were abrogated in the FxrΔPC mice (P=0.0006). Total n=7/group. (D) Ileal organoids derived from the FxrΔPC mice did not show reduced percentages of Paneth cells/organoid when treated with DCA or GW4064. (B, D): Results were from 3 independent experiments, with each experiment containing 20 organoids/group. (A-D) Statistical analysis between 2 groups was performed by Mann-Whitney test. Statistical analysis between more than 2 groups was performed by Kruskal-Wallis test. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; ****: P<0.0001. Error bars represent standard deviations.
