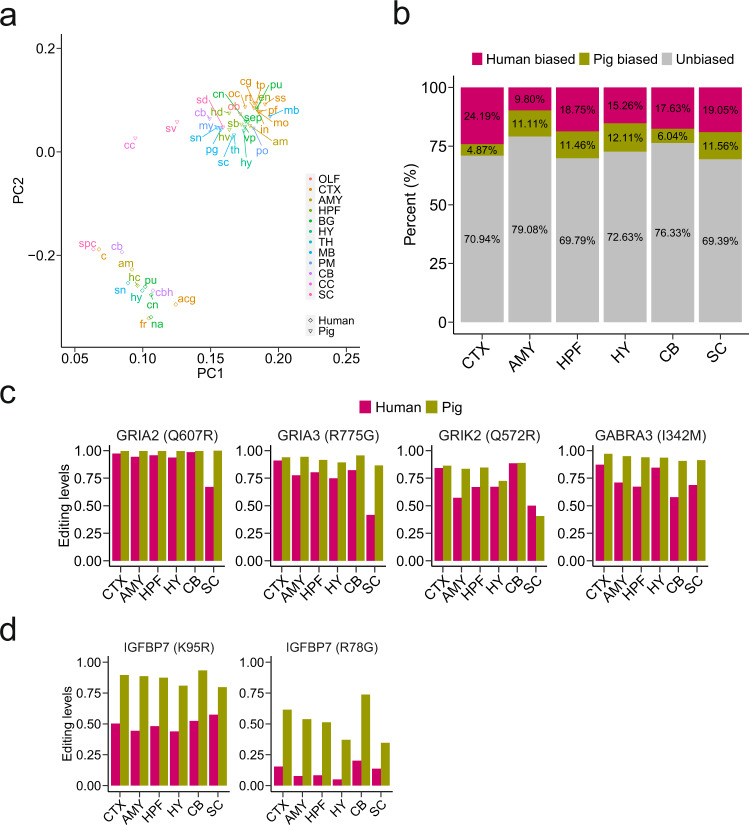
Fig. 5. Conserved A-to-I editing sites between the pig and human brain.
a PCA on editing levels of conserved editing sites across various brain regions between pig and human. The subregions in human brain are as follows: amygdala, am; anterior cingulate cortex, acg; caudate, cn; cerebellar hemisphere, cbh; cerebellum, cb; cortex, c; frontal cortex, fr; hippocampus, hc; hypothalamus, hy; nucleus accumbens, na; putamen, pu; spinal cord, spc; and substantia nigra, sn. The subregions in pig brain are as follows: olfactory bulb, ob; cingulate cortex, cg; motor cortex, mo; prefrontal cortex, pf; retrosplenial cortex, rt; somatosensory cortex, ss; temporal lobe, tp; insula cortex, in; occipital lobe, oc; amygdala, am; entorhinal cortex, en; hippocampus dorsal, hd; hippocampus ventral, hv; subiculum, sb; caudate nucleus, cn; putamen, pu; septum, sep; ventral pallidum, vp; hypothalamus, hy; thalamus, th; midbrain, mb; periaqueductal gray, pg; superior colliculus, sc; substantia nigra, sn; medulla oblongata, my; pons, po; cerebellum, cb; corpus callosum, cc; spinal cord dorsal, sd; and spinal cord ventral, sv. The subregions are organized into 12 main regions, including Olfactory bulb, OLF; Cerebral cortex, CTX; Amygdala, AMY; Hippocampal formation, HPF; Basal ganglia, BG; Hypothalamus, HY; Thalamus, TH; Midbrain, MB; Pons and medulla, PM; Cerebellum, CB; Corpus callosum, CC; and Spinal cord, SC. b Comparisons of conserved editing sites across six brain regions, including the cerebral cortex, amygdala, hippocampal formation, hypothalamus, cerebellum, and spinal cord. c A number of highly edited sites in both two species were highlighted. d Two pig-biased recoding sites located in insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7).