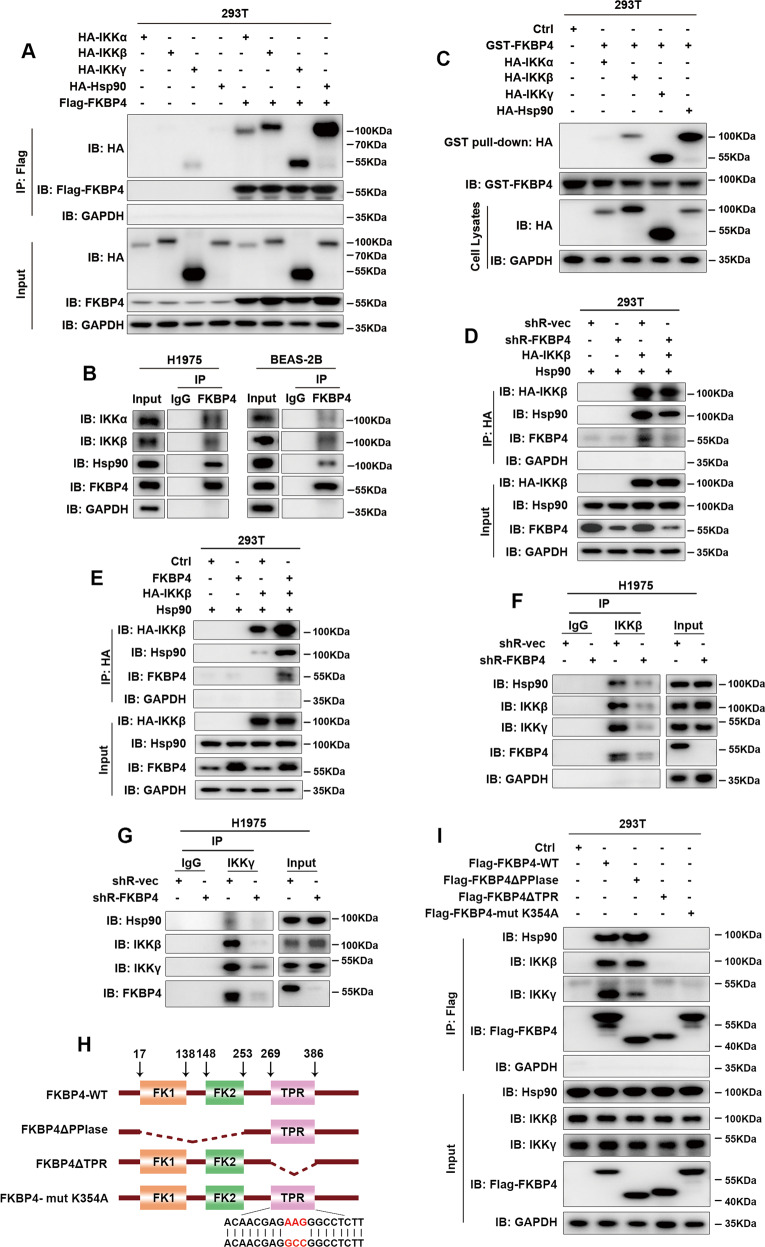
Fig. 4. FKBP4 promotes Hsp90/IKK association and IKK complex assembly.
A Co-IP analysis of 293T cells transfected with Flag-FKBP4 and the indicated plasmids, namely, HA-IKKα, HA-IKKβ, HA-IKKγ, and HA-Hsp90. FKBP4 interacted with all IKK complex subunits and Hsp90 under transfection conditions. B Co-IP analysis of endogenous FKBP4 interacting with endogenous IKKα, IKKβ, and Hsp90 in H1975 and BEAS-2B cells. C Pull down of HA-IKKβ, HA-IKKγ, and HA-Hsp90 by GST-tagged FKBP4. D Co-IP analysis of 293T cells with or without FKBP4 silencing and transfected with HA-IKKβ and Hsp90. FKBP4 knockdown impaired the interaction between Hsp90 and IKKβ under transfection conditions. E Co-IP analysis of 293T cells overexpressing or not overexpressing FKBP4 and transfected with HA-IKKβ and Hsp90. FKBP4 overexpression promoted the interaction between Hsp90 and IKKβ under transfection conditions. F Co-IP analysis showed that FKBP4 depletion blocked the interaction between Hsp90 and IKKβ in H1975 cells. G Co-IP analysis showed that FKBP4 depletion prevented the binding of IKKγ to IKKβ in H1975 cells. H Schematic illustration of FKBP4, showing the wild-type, truncation mutants (deleted PPIase or TPR domains), and point mutant (K354A) of FKBP4. I Co-IP analysis of the interaction between Hsp90/IKK and FKBP4 mutants in 293T cells transfected with the Flag-FKBP4 wild-type plasmid or plasmids harboring different mutations.