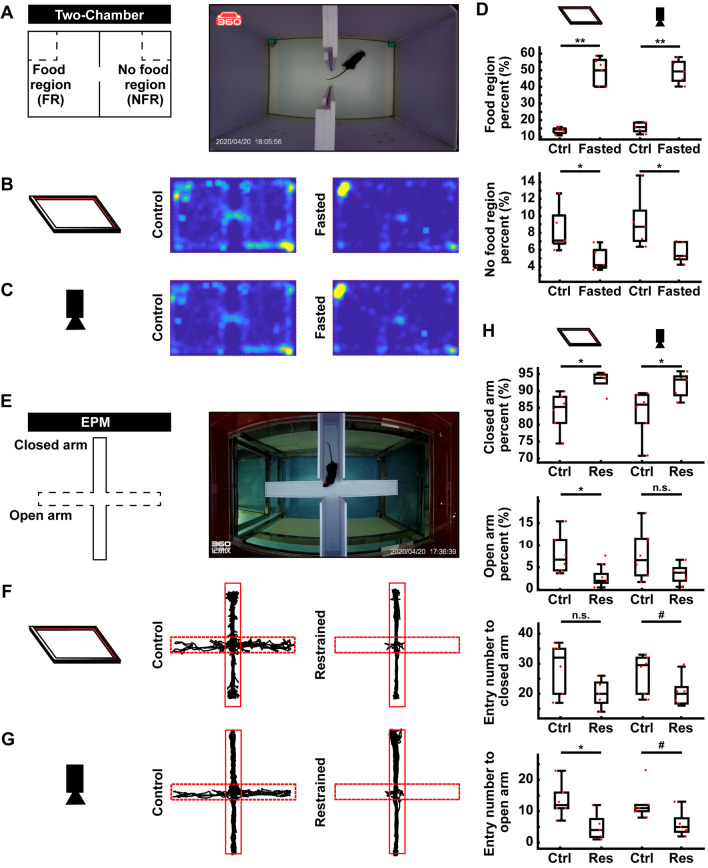
Fig. 3.
Open-loop paradigms in the AIBM system. A Schematic (left) and photograph (right) of the two-chamber paradigm. B Representative trajectories of control (left) and the restrained (right) groups collected by the infrared position detector. C Representative trajectories of the control (left) and restrained (right) groups collected by video camera. D Percentages of time spent in the food (upper) and no-food (lower) region; data collected with the infrared detector (left) and video camera (right). FR, food region; NFR, no-food region. E Schematic (left) and photograph (right) of the elevated plus maze (EPM) paradigm. F Representative trajectories from control (left) and restrained (right) groups collected by the infrared detector. G Representative trajectories from control (left) and restrained (right) groups collected on a video camera. H Behavioral parameters in the EPM paradigm. Percentages of time spent in, and the number entries into, the closed/open arm. Data were collected with the infrared position detector (left) and video camera (right). Res, restrained. n = 5 mice in each group. #P <0.1, *P <0.05, **P <0.01, ***P <0.001, experimental vs control groups, rank sum tests.