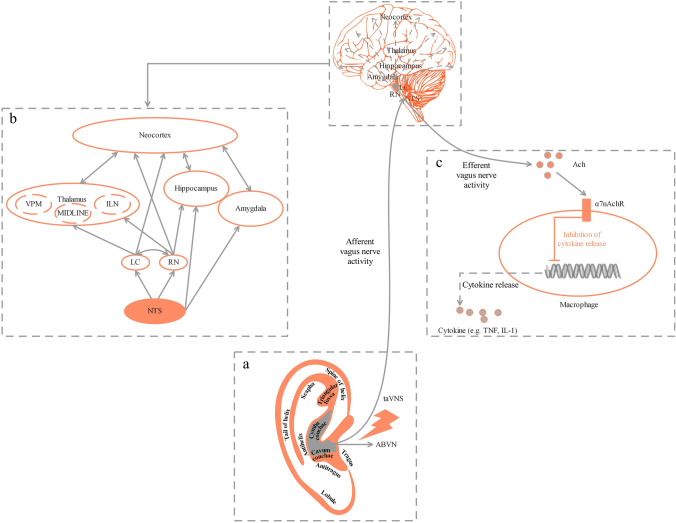
Fig. 2.
Potential mechanism of taVNS. A The external ear and its hypothesized cutaneous innervation by the ABVN. B Modulation of brain networks mainly depends on the extensive fibrous connections formed by ABVN projections to multiple brain regions through the NTS to regulate neuroendocrine, emotional, and cognitive functions. C The balance of the production of cytokines depends on the wiring of CAP [87, 88]. CNS, central nervous system; CAP, cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway; VPM, ventralis posteromedialis nucleus; MIDLINE, midline thalamic nuclei; ILN, intralaminar nuclei; LC, locus coeruleus; RN, raphe nuclei; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; ABVN, auricular branch of the vagus nerve; taVNS, transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation; ACh, acetylcholine; α7nAChR, α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL-1, interleukin-1.