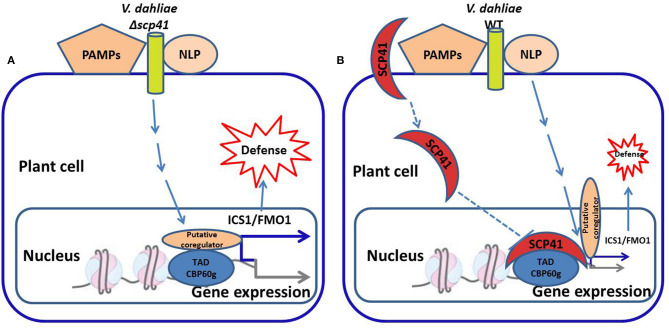
Figure 2.
Model for VdSCP41-mediated suppression of Arabidopsis defense during Verticillium dahliae infection (Qin et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2018). (A) During the infection of V. dahliae, the plant transcription factor CBP60g induces the expression of immune-related genes and the defense response. (B) VdSCP41, a V. dahliae effector protein, is transported to the nucleus of plant cells and directly targets CBP60g, which interferes with the transcription factor activity and thus suppresses plant immunity. WT, wildtype, PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns, NLP, nuclear localization protein, SCP41, secretory protein 41, ICS1, isochoric acid synthase 1, FMO1, flavin monooxygenase 1, TAD, transcription activation domain, CBP60g, calmodulin binding protein 60 g.