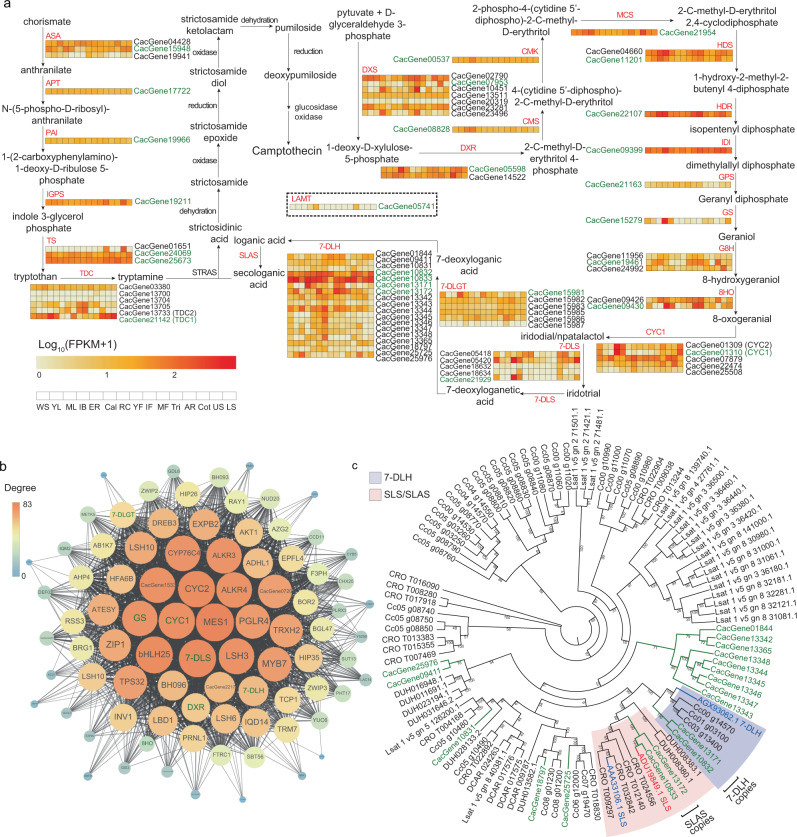
Fig. 2. Genes involved in camptothecin biosynthesis.
a A simplified representation of the camptothecin biosynthetic pathway. Top hits for pathway genes identified by blast and pathway genes in the co-expression network are highlighted in green. The expression value for each gene is indicated in color on a log10(FPKM + 1) scale for fifteen tissues: whole seedlings (WS), young leaf (YL), mature leaf (ML), immature bark (IB), entire root (ER), callus (Cal), root culture (RC), young flower (YF), immature fruit (IF), mature fruit (MF), trichomes (Tri), advance roots (AR), cotyledons (Col), upper stem (US), lower stem (LS). b The WGCNA “grey60” module related to camptothecin biosynthesis as represented by a node and edge graph. Connection strength is represented by edge width (edge weights < 0.25 are omitted). c A phylogenetic tree of all candidate genes in the CYP72A subfamily. The sequences shown in blue and red indicate previously published 7-DLH and SLS genes in C. roseus while those in green show candidate genes identified in the C. acuminata V3.0 genome.