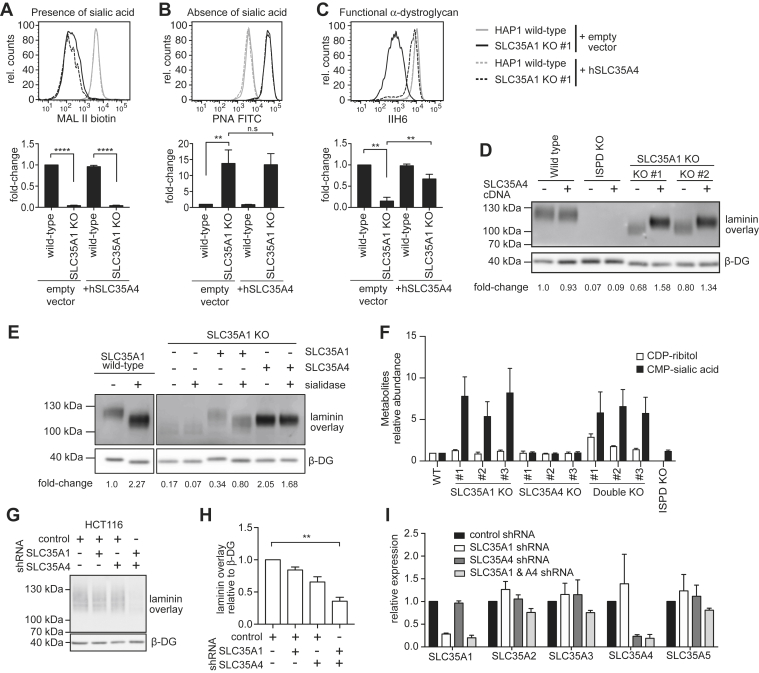
Figure 3.
SLC35A1 and SLC35A4 perform redundant functions during the formation of the laminin-binding glycan, but SLC35A1 is crucial for sialylation.A–C, flow cytometry with MAL II lectin, peanut agglutinin (PNA), and the antibody IIH6 was performed on wildtype or SLC35A1 KO HAP1 cells that were transduced with a lentivirus driving expression of murine Slc35a4 complementary DNA or an empty vector control. Bar graphs underneath flow cytometry histograms represent means ± SEM of the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) observed in three independent experiments. Note that the presented experiment was performed in parallel to the experiment presented for Figure 1, explaining why the empty vector controls are identical. D, laminin overlay performed on wildtype, SLC35A1 KO and ISPD KO HAP1 cells upon expression of SLC35A4 (or an empty vector control). E, samples from the indicated HAP1 cell lines were subjected to laminin overlay or β-dystroglycan Western blot. Where indicated, sialidase digest was performed before laminin overlay. The presented data are from one gel, where two lanes in the middle were removed. F, quantification of CDP-ribitol and CMP-sialic acid (i.e., CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid) in the indicated cell lines. Relative intracellular CDP-ribitol and CMP-sialic acid levels in HEK293 cells knocked out for SLC35A1 and/or SLC35A4 as measured by LC/MS. The ISPD KO cells were used as a negative control for CDP-ribitol measurements. Means ± SEM of three independent experiments are shown, and values were normalized within each experiment to levels in wildtype (control) cells. G and H, laminin overlay and β-dystroglycan Western blot (G) as well as quantitative evaluation of three independent experiments (H) obtained in HCT116 cells that express SLC35A1, SLC35A4, or nonsilencing control shRNAs. I, RT-quantitative PCR analysis for the indicated mRNAs in cell lines described for G and H. HEK293, human embryonic kidney 293 cells; ISPD, isoprenoid synthase domain–containing protein; MAL II, Maackia amurensis lectin II.