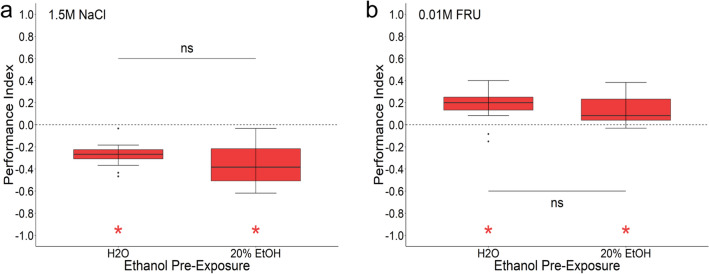
Figure 6.
Pre-exposure to ethanol does not change aversive and appetitive olfactory learning. Before the larvae were conditioned, they were separated from their food and treated for 20 min with either water or 20% ethanol. They were then washed and trained with the odors AM and BA and either 1.5 M NaCl or 0.01 M fructose as a teaching signal. (a) Larvae treated with water and 20% ethanol both showed an aversive odor-salt memory (one-sample t test, pwater < 0.001, ppre-EtOH < 0.001) that was not different from each other (paired t-test, p < 0.112). Sample size for each box plot is n = 15. (b) Larvae treated with water and 20% ethanol both showed an appetitive odor-fructose memory (one-sample t test, pwater < 0.001, ppre-EtOH < 0.001) that was not different from each other (paired t-test, p < 0.484). Sample size for each box plot is n = 15. Differences against zero are indicated in red at the bottom of each panel. Significant differences of two groups are specifically indicated with an asterisk. Non-significant results are not indicated. Preference scores and statistical tests underlying the different indices are documented in the Supplementary material.