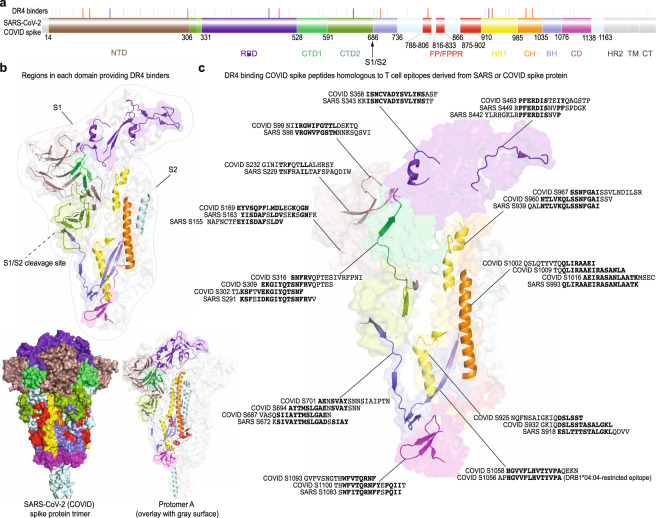
Fig. 7. DR4 binders derived from the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID) S protein.
a Mapping DR4 binders to different domains of the S precursor. Each vertical bar indicates the exact starting position of a DR4-binding S peptide (the colors of the vertical bars match Fig. 5 and Supplementary Table 1). NTD N-terminal domain, RBD receptor-binding domain, CTD1/2 C-terminal domain 1/2 (or subdomain 1/2, SD1/2), FP/FPPR fusion peptide and fusion peptide proximal region [53], HR1/2 heptad repeat 1/2, CH central helix, BH b-hairpin [54], CD connector domain (or subdomain 3, SD3), TM transmembrane domain, CT cytoplasmic tail. b Regions on protomer A of the COVID S protein that contain DR4-binding peptides. The cartoon (over surface) presentation of each domain uses the same color scheme as in a. c Comparison of SARS S-derived DR4 binders with previously identified candidate DR4-restricted T cell epitopes [6, 13] that are from either the SARS-CoV-1 (SARS) or SARS-CoV-2 (COVID) S protein. Identical or conserved residues are bolded. The starting position of each COVID S or SARS S peptide and the cartoon (over surface) presentation of the corresponding COVID S peptide on protomer A are indicated. The structure [47] was obtained from PDB ID 6XR8 with an emphasis on protomer A. The individual showing positive CD4+ T cell responses to the SARS-CoV-2 S epitope carried DR4 allelic subtype DRB1*04:04 [6], as indicated in parentheses.