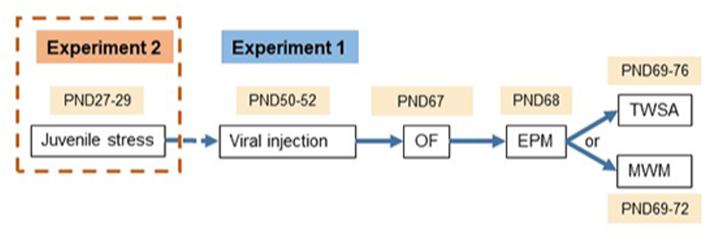
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of the experimental design for the analysis of GAD65 knock down effects on anxiety and learning behavior. Following viral injections on PND 50–52, rats were assigned to two experimental paradigms: Experiment (1), to assess the effects of GAD65/67 expression reduction on emotional behavior, learning and memory. Viral gene reduction was conducted in naïve rats at PND 50–52. Separate animal groups were injected in the dDG with shGAD65/shshCTR (N = 25/22), shGAD67/shCTR (N = 13/13), and in the vDG (N = 21/17 and N = 18/15, respectively); then tested in the OF (PND 67), EPM (PND 68), followed by either TWSA test (PND 69–76) or MWM (PND 69–72). For the latter two tests, the groups were split as follows: TWSA, injected to the dDG: shGAD65/shCTR (N = 11/8) and shGAD67/shCTR (N = 5/5); injected to the vDG: shGAD65/shCTR (N = 11/8) and shGAD67/shCTR (N = 10/7); MWM, injected to the dDG: shGAD65/shCTR (N = 10/10) and shGAD67/shCTR (N = 8/8); injected to the vDG: shGAD65/shCTR (N = 10/9) and shGAD67/shCTR (N = 8/8). Experiment (2), viral intervention was performed in rats pre-exposed to juvenile stress (JVS) at puberty (PND 27–29) before viral injection at adulthood with either shCTR (JS + shCTR) or shGAD65 (JS + shGAD65), in the dDG only on PND 50–52. Another group of rats that did not undergo any surgical procedure was included as a naïve control and split into exposed and non-exposed to JVS ((NAIVE group (N = 24), NAÏVE + JS, N = 25)). Behavioral testing was conducted as described for paradigm 1. For TWSA and MWM, groups were split as follows: TWSA (NAIVE = 10, NAIVE + JS = 10, JS + shCTR = 11, JS + shGAD65 = 9) or MWM/physiology tests (NAIVE = 14, NAIVE + JS = 15, JS + shCTR = 11, JS + shGAD65 = 11). In vivo LTP was conducted two weeks after the last behavior testing on PND 90. All behavioral experiments were conducted by experimenters blinded for which viral vector was injected.