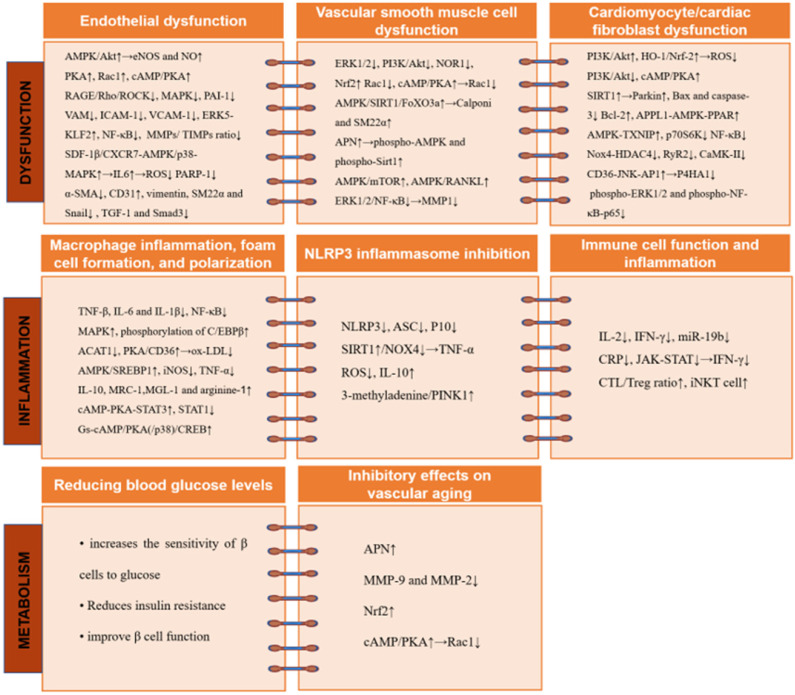
Figure 2.
The cardiovascular protective effects of GLP-1RA involve multiple molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways. GLP-1RA inhibit endothelial cell dysfunction while attenuating abnormal migration, proliferation, and apoptosis in VSMCs. In addition, GLP-1RA decrease macrophage inflammation and blocks NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Further, GLP-1RA protect against vascular aging and maintains the metabolic homeostasis of cardiomyocytes. Abbreviations: ACAT: acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; APN: adiponectin; APPL: activating the leucine zipper motif'; ASC: apoptotic speck containing protein; Bax: Bcl-2-associated x; Bcl: B-cell lymphoma; CaMK: calmodulin-dependent protein kinase; cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CD31: cell adhesion molecule; C/EBP β: CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β; CREB: cAMP response element binding-protein; CRP: C-reactive protein; CTL: cytotoxic T lymphocyte; CXCR: C-X-C motif receptor; eNOS: endothelial NO synthase; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FOXO: forkhead box O; HDAC4: histone deacetylase 4; HO-1: heme oxygenase-1; ICAM-1: intracellular adhesion molecule-1; IFN: interferon; IL: interleukin; iNKT: invariant natural killer T; iNOS: inducible NOS; JAK: Janus kinase; JNL: Jun NH2-terminal kinase; KLF2: Kruppel-like factor 2; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinases; MGL-1: macrophage galectin-1; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase; MRC-1: mannose receptor-1; mTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin; NF-κB: a nuclear factor-κB; NLRP3: Nod-like receptor protein 3; NOR1: neuron-derived orphan receptor 1; Nox4: NADPH oxidase 4; Nrf2: nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; ox-LDL: oxidized-LDL; PAI: plasminogen activator inhibitor; PARP-1: poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; PINK1: the mitochondrial kinase; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKA: protein kinase A; PPAR: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; P10: cleaved caspase 1; P4HA1: prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit alpha-1; p70S6K: p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase; Rac1: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1; RAGE: receptor AGE; RANKL: receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand; Rho: the small GTPase; ROCK: Rho kinase; ROS: reactive oxygen species; RyR2: the type 2 ryanodine receptor; SDF: stromal cell-derived factor; SREBP1: element binding transcription factor 1; SIRT: sirtulin; α-SMA: alpha smooth muscle actin; SM22α: sensitive 22 kDa actin-binding protein of the calponin; STAT: cAMP-PKA-signal transducers and activators of transcription; TGF: transforming growth factor; TIMP: tissue inhibitor of MPs; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; Treg: regulatory T cell; TXNIP: AMPK-Thioredoxin-interacting protein; VAM: vascular adhesion molecule; VCAM-1: vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; VSMC: vascular smooth muscle cells.