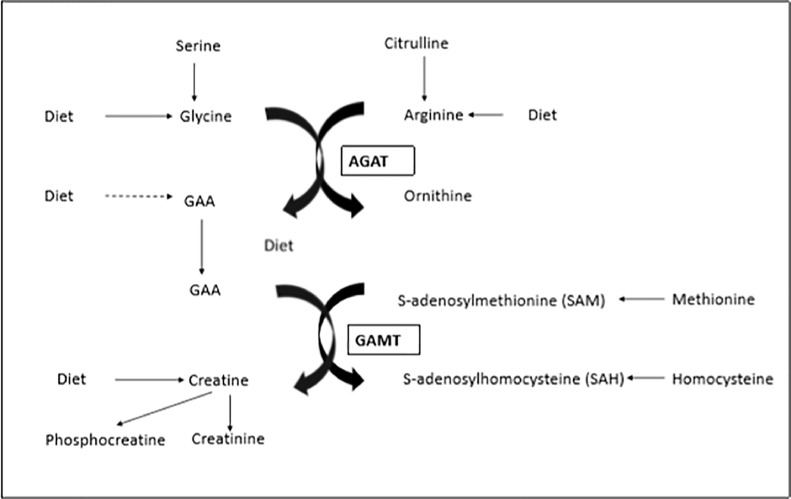
Figure 1.
Synthesis of GAA from glycine and arginine and conversion to creatine.1 Adapted from Ostojic (2015) GAA is synthesized from the amino acids glycine and L-arginine; the reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme L-arginine–glycine amidinotransferase (AGAT). AGAT is located mainly in the kidneys and pancreas. After transport mainly to the liver GAA is methylated to form creatine. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase (GAMT) and requires transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) to GAA, to form creatine and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH).