FIGURE 1.
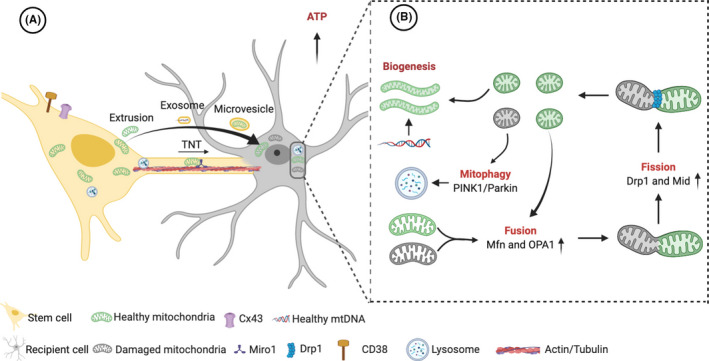
Transfer routes and protection mechanisms of stem cell‐derived mitochondria. (A) The routes of healthy mitochondria transfer from stem cells to recipient cells with dysfunctional mitochondria include TNT formation, release of extracellular microvesicles and mitochondrial extrusion. Exosomes might transfer organelle fragments (such as protein complexes of the mitochondrial electron transfer chain), mtDNA and ribosomes. The permanent cell fusion and formation of synkaryons are scarce in co‐culture conditions and in vivo, which are not drawn in the figure. (B) Stem cell‐derived mitochondria might rescue aerobic respiration and energy metabolism directly, regulate mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis, optimize mitochondrial fission and fusion, and decrease the mtDNA mutation load. Cx43, connexin 43; Drp 1, dynamin‐related protein 1; Miro1, Mitochondrial Rho‐GTPase 1; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; Mfn, mitofusin; Mid, mitochondrial dynamics protein; OPA1, optic atrophy 1; PINK1, putative kinase 1; TNT, Tunneling nanotube. (Figure Created with BioRender.com)
