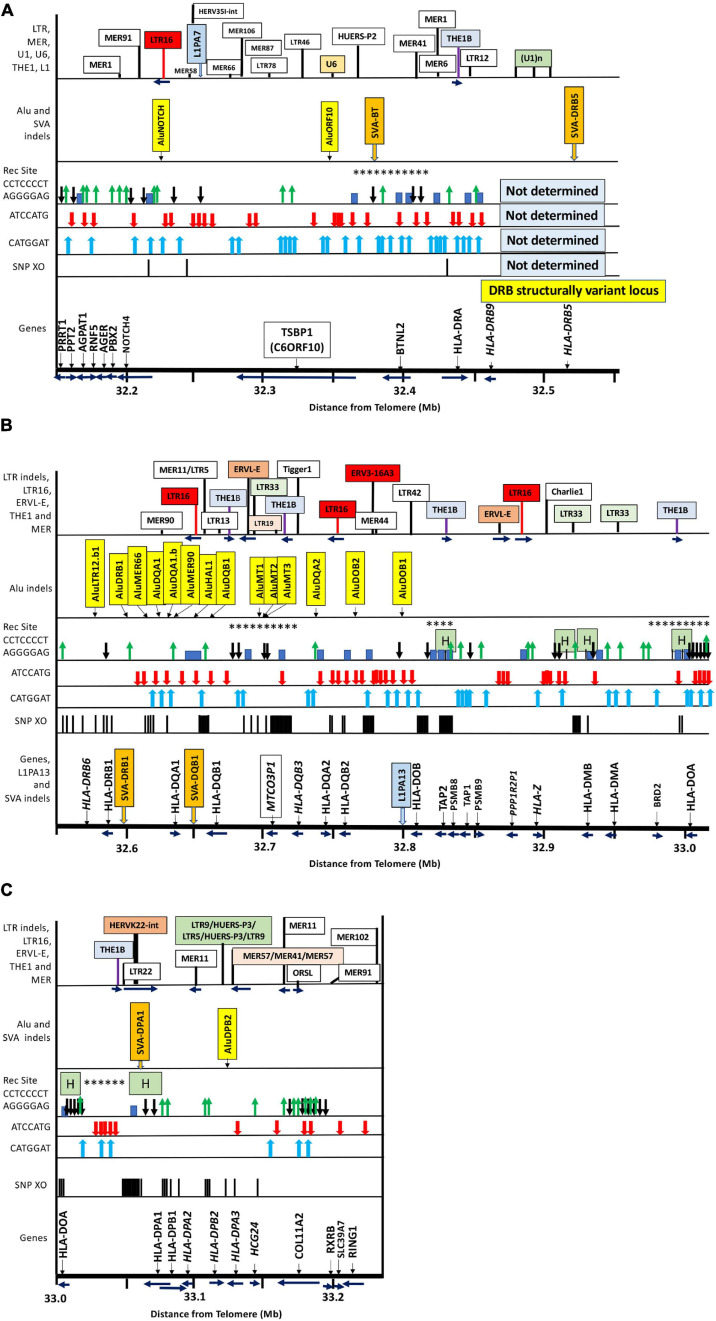
FIGURE 1.
Locations of gene markers (pseudogenes in italics), SNP-density crossover points (haplotype shuffling), recombination sites (Rec Site), PRDM9 partial binding and suppression motifs, Alu and SVA indels, and particular repeat elements used as location tags within ∼1 Mb of MHC class III/class II genomic sequence from PRRT1 to RING1 and the nucleotide position 32.150 to 33.22 Mb distance from telomere on chromosome 6 (sequence NC_000006 at NCBI, UCSC, ENSEMBL): (A) The MHC class III/II boundary from 32.15 to 32.55 Mb including the Class III genes PRRT1 to BTNL2 and the Class II genes, HLA-DRA and HLA-DRB9 and HLA-DRB5– within the DRB structural variant locus; (B) the MHC class II region from 32.55 to 33.01 Mb with the location of the duplicated HLA class II genes from HLA-DRB6 to HLA-DOA; (C) the MHC class II region from 33 to 33.22 Mb with the location of the duplicated HLA class II genes from HLA-DOA to HLA-DPA3 with the extended centromeric region containing the COL11A2, RXB, SLC3A7 and RING1 genes. Each Figure A to C contains labeled boxes showing the following comparative items: Genomic position of SNP-density crossover points (SNP XO) indicated by vertical black lines. The genomic position of the PRDM9-suppression sequence motifs ATCCATG and CATGGAT indicated by red and blue vertical arrows, respectively. The ‘Rec Site’ boxes represent the putative regions of ancestral meiotic recombinations and gene conversions as indicated by the PRDM9 partial binding motif CCTCCCCT (black vertical arrow with head down) and its complimentary sequence AGGGGAG (green vertical arrow with head up). The blue blocks are putative recombination sites identified by Lam et al. (2013). The H green boxes are ‘hotspots’ identified by Jeffreys et al. (2001), Kauppi et al. (2005), Kong et al. (2010) and Pratto et al. (2014), and highlighted in the NCBI browser (Table 7). The asterix (∗) are the meiotic recombination positions identified in sperm studies by Cullen et al. (1997, 2002). The ‘Alu indels’ boxes show the location of the dimorphic Alu listed in Table 3, and the dimorphic SVA are shown in the ‘Alu indels’ boxes for (A) and (C) and in the ‘Genes’ box for (B). The top boxes of ‘LTR indels’ show the genomic position of selected TE as location tags for orientation and because some of them such as MER1 and MER11 harbor PRDM9 motifs or because some such as LTR16, LTR19, LTR33 and THE sequences have a possible role in recombination initiation and/or suppression.