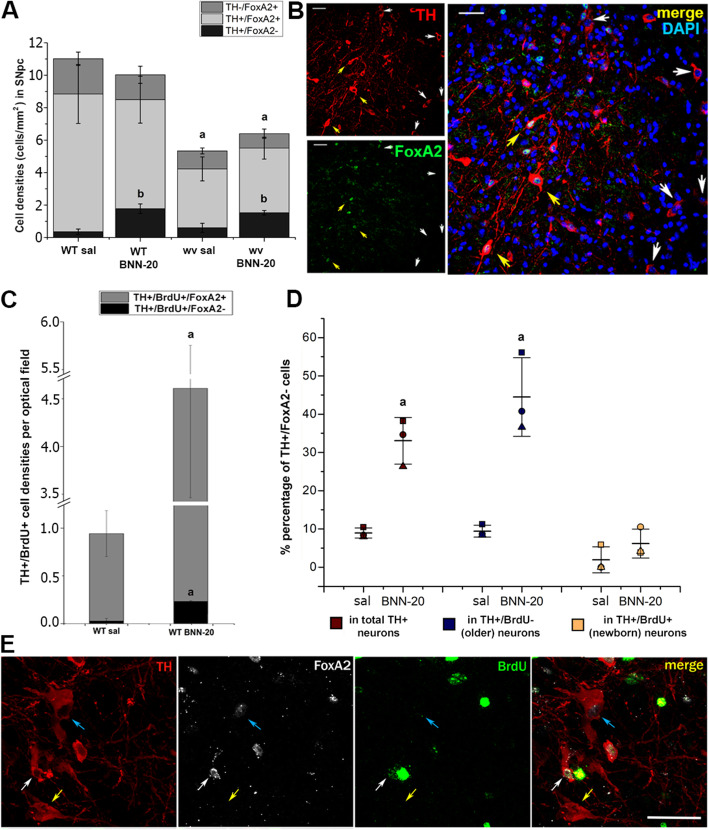
Fig. 3.
FoxA2 expression in the dopaminergic cell lineage of the SNpc. A Cell densities of the different subpopulations within the dopaminergic lineage (based on expression of TH and FoxA2) A in the SNpc of wild-type (WT) and “weaver” (wv) mice that received BNN-20 or saline (sal) from P14 to P60 and Β a characteristic example of immunostaining (with some of the TH+/ FoxA2− cells indicated by white arrows, and some of the TH+/FoxA2+ cells indicated by yellow arrows) [scale bar= 50 μm. a: decreased total TH+ cell densities (p < 0.05) compared to WT BNN-20 and WT sal groups (F = 7.94, p = 0.023 for genotype); b: increased TH+/FoxA2− densities (p < 0.05) compared to WT and wv sal groups (F = 25.971, p = 0.001 for drug), using two-way ANOVA followed by LSD post hoc analysis. n = 3 animals per group. Error bars are SEMs.]. C TH+/BrdU+ cell densities per optical field in the SNpc of the WT sal and WT BNN-20 groups, also showing the co-expression of FoxA2 [a: increased TH+/BrdU+/FoxA2+ and TH+/BrdU+/FoxA2− densities compared to WT sal; p < 0.05, using Student’s t test, n = 3 animals per group. Error bars are SEMs]. D Percentage of the newly described TH+/FoxA2− cells within the pools of total TH+ cells (in dark red), older (TH+/BrdU−, in blue), and newborn (TH+/BrdU+, in yellow) dopaminergic neurons in the WT SNpc post-administration of BNN-20 or saline (sal) (P14–P60) [a: increased % TH+/FoxA2− percentage compared to WT sal; p < 0.05, using Student’s t test, n = 3 animals per group. Error bars are SDs]. E A characteristic example of immunostaining indicating the 3 dopaminergic subpopulations of the SNpc: TH+/BrdU+/FoxA2+ (white arrow), TH+/BrdU−/FoxA2+ (cyan arrow), and TH+/BrdU−/FoxA2− (yellow arrow) [scale bar= 50 μm]