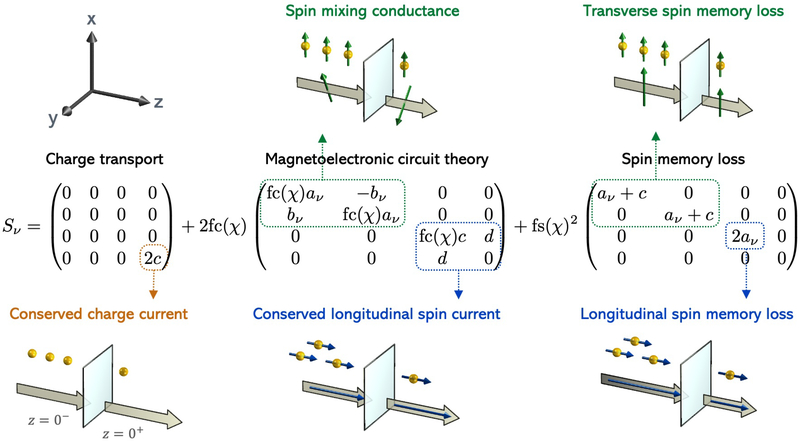
FIG. 13.
Breakdown of the Sν matrices (ν ∈ [i-r, t]) when spin or charge accumulations drive transport at interfaces. The matrix St determines the spin and charge accumulation μ at the interface (see Eq. 28). The symmetric response determines the average spin current at the interface (see Eq. 29). The antisymmetric response ΔS = Si-r −St determines the difference in spin current Δjz across the interface (see Eq. 30). The matrix column specifies the spin and charge accumulations at z = 0± while the row gives the components of μ, , or Δjz, depending on whether Eq. 28, Eq. 29, or Eq. 30 is used. The images depict the charge accumulations (gold spheres) or the spin accumulations (gold spheres with arrows) that drive the system and the resulting spin currents at z = 0±, where block arrows denote flow direction and tubular arrows denote spin direction.