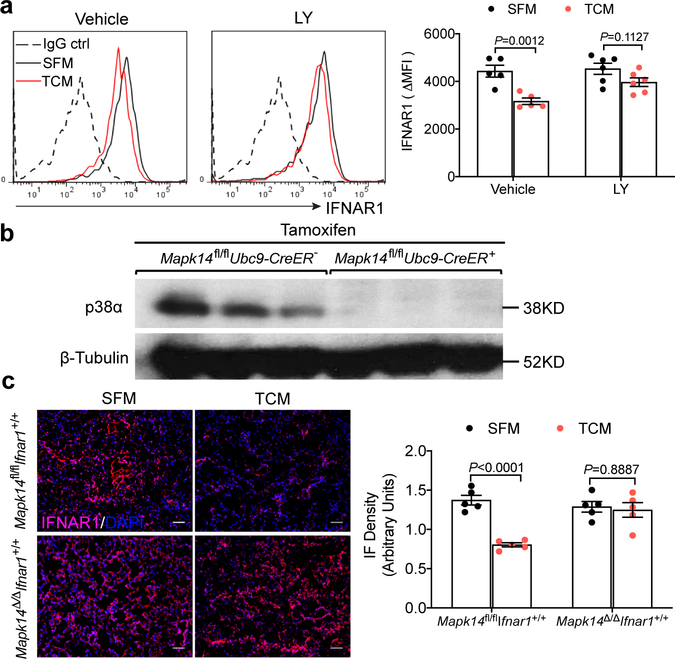
Extended Data Fig. 3: p38α inhibition or gene deletion impede tumor derived factors-induced downregulation of IFNAR1.
a. A representative flow cytometry analysis (left) and the quantification of surface IFNAR1 level (right) in WT lung fibroblasts pretreated with vehicle (DMSO) or p38 inhibitor Ralimetinib (LY2228820, 4 μM for 2 hr) followed by SFM, or B16F10 TCM treatment for additional 2 hr. Quantitative data shown as mean±SEM (n=5,and n=6 biologically independent samples in Vehicle and LY treated group). Two-way ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparisons test were performed. b. A representative western blot analysis of total p38α protein level in the lung tissues of Mapk14fl/fl Ubc9-CreER- and Mapk14fl/flUbc9-CreER+ mice after tamoxifen treatment. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. c. A representative immunofluorescence staining of IFNAR1 (left) and the quantification of IFNAR1 level (right) in the lung tissues from Mapk14 competent mice (Mapk14fl/fl) and Mapk14 deleted mice (Mapk14Δ/Δ) treated with SFM or B16F10 TCM (100 μl i.v., 3x per week for 3 weeks). Scale bar: 100 μm. Quantitative data shown as mean±SEM (n=5 mice per group). Two-way ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparisons test were performed.