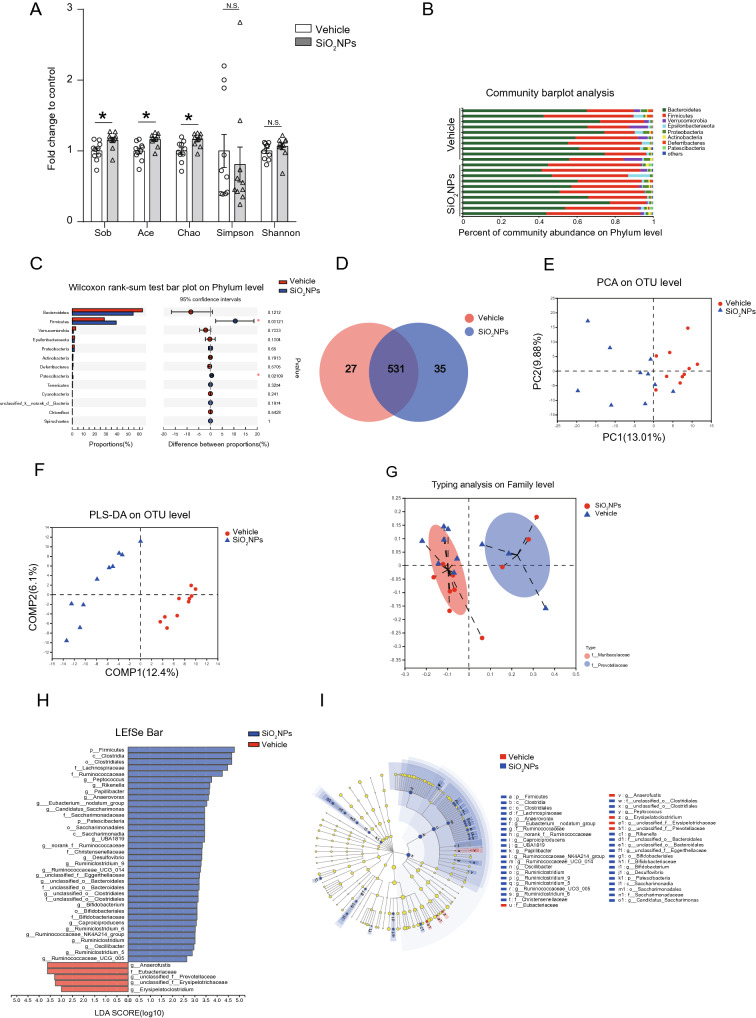
Fig. 3.
Oral exposure to SiO2NPs caused the disturbance of gut microbiota and their associated biological functions. The fecal samples of two groups were collected and subjected to 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene sequencing. A Sobs, Ace, Chao, Simpson, and Shannon were determined to assess the α-diversity of gut microbiota. Data were reported as mean ± S.E.M. Statistical analysis was calculated by using independent student-t test. Asterisk * indicated P < 0.05. B The percent of community abundance on phylum level was detected in two groups. The differences on the community abundance on phylum level were analyzed and shown in (C). D Venn diagram showed the overlap of core microbiota between vehicle group and SiO2NPs-treated group. E The dissimilarities in microbial composition on OTU level was determined by principal component analysis (PCA). F Partial least squares discrimination analysis (PLS-DA) was used to detect the gut microbial community compositions between two groups. Bacterial clades and biologically consistent difference (LDA score > 2.0) were assessed by Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) coupled with effect size (LEfSe) (H, I). Typing analysis on family level was shown in (G)