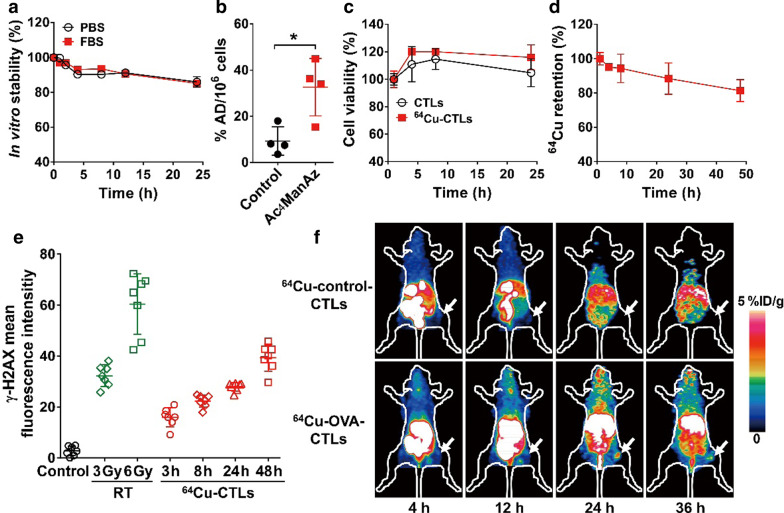
Fig. 3.
Metabolic 64Cu-radiolabeling of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and in vivo small-animal PET imaging. a In vitro stability of 64Cu-labeled NOTA-DBCO in PBS and FBS (n = 3). b Binding specificity of 64Cu-labeled NOTA-DBCO with Ac4ManNAz-incubated CTLs (n = 4). The results are expressed as percentage administered dose per million cells (%AD/106 cells). c Cell viability of unlabeled CTLs or 64Cu-labeled CTLs (64Cu-CTLs) after culturing for various times (n = 5). d 64Cu retention on the surfaces of the CTLs after incubating in cell culture medium for various times (n = 4). e DNA damage of untreated CTLs (control), CTLs treated with 3 or 6 Gy of X-ray irradiation (RT), or 64Cu-labeled CTLs (3, 8, 24, and 48 h after labeling) as measured using γH2AX immunofluorescence staining (n = 7). f Small-animal PET images of 64Cu-labeled control-CTLs and 64Cu-labeled OVA-specific CTLs (OVA-CTLs) in B16-OVA tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice at 4, 12, 24, and 36 h postinjection. Tumors are indicated by white arrows. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *, P < 0.05