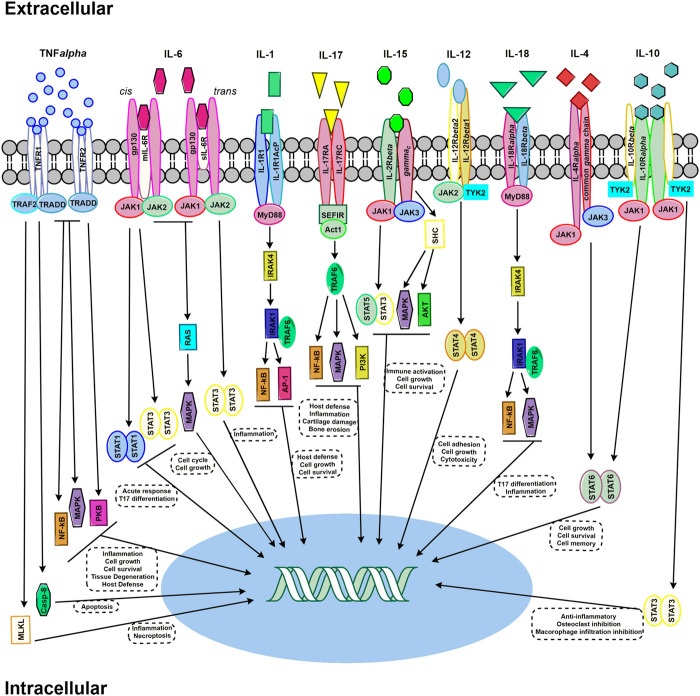
FIGURE 4.
Select signaling pathways in RA. TNF-α signaling pathways required either TNFR1 or TNFR2 trimers. Signaling via TNFR1 pathway, upon TRADD binding without TNFR2, triggers cell death by either Casp-8 or MLKL. The recruiting of TRAF2 activates multiple signaling pathway cascade activation – including MAPK, NF-kB, and PKB. IL-6 signaling can occur through either mIL-6R classic signaling and of sIL-6R trans signaling. JAK activation occurs through both signaling mechanism and activating STAT and RAS/MAPK. IL-1 signaling through IL-1R1 via MyD88 which activates IRAK4 and subsequently IRAK1 bound to TRAF6 – leading to the activation of NFkB and AP1. IL-17 binds to an IL-17RA and IL-17RC receptor dimer. The SEFIR conserved signaling domain recruits Act1, which recruits TRAF6 and subsequently activates NF-kB, MAPK, and PI3K signaling pathways. IL-15 signaling can occur through JAK/STAT activation resulting in STAT3/STAT5 heterodimer formation, or activation through SHC which then results in activating MAPK and AKT. IL-12 signaling occurs through a heterodimer receptor consisting of IL-12Rβ1 and IL-12Rβ2 which activates JAK2 and TRK2 – leading to STAT4 dimer activation. IL-18 signaling results from the recruiting of MdD88 to the IL-18Rα and IL-18Rβ heterodimer, activating IRAK4 and thus TRAF6, which subsequently activates NF-kB and MAPK pathways. IL-4 signaling occurs the JAK/STAT activation via JAK1 and JAK3 binding to the IL-4Rα and common gamma-chain, respectively. IL-10 signal transduction results from both JAK1 binding to IL-10Rα and TYK2 binding to IL-10Rβ – which activates STAT3 in homodimer form.