Figure 1.
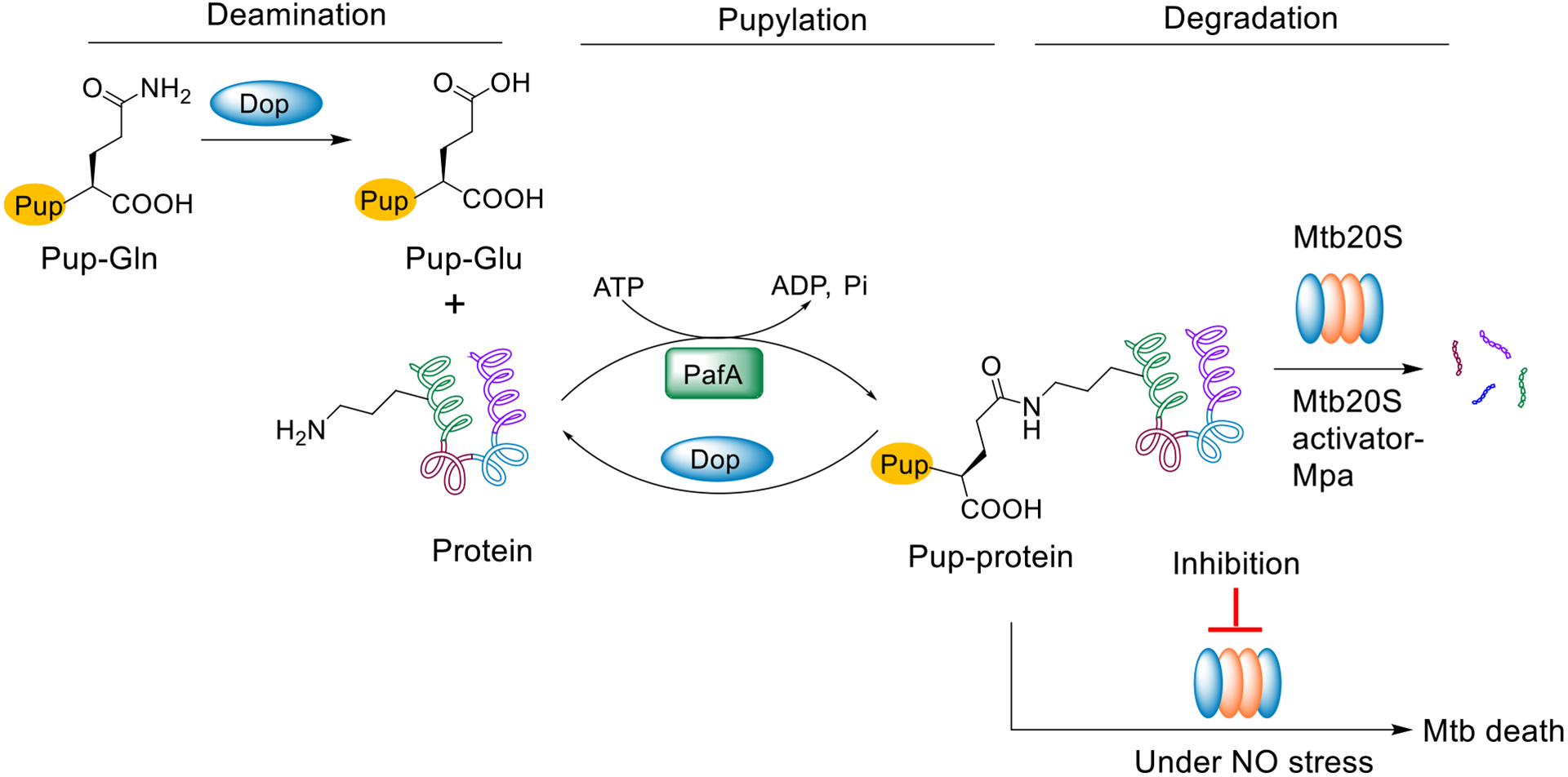
Schematic representation of Pup-proteasome system (PPS) in M. tuberculosis. Pup is expressed with a C-terminal glutamine (Pup-Gln), which is deamidated to glutamate (PupGlu) by Dop. PafA, a Pup ligase, then catalyzes the formation of an isopeptide bond between the C-terminal γ-carboxylate of Pup-Glu and the lysine ε-amino group of a protein substrate. The pupylated protein is recognized and unfolded by Mpa and degraded by the Mtb 20S proteasome. Alternatively, Dop can rescue the pupylated substrate by cleaving the specific isopeptide bond. Inhibition of the Mtb proteasome under NO stress (mimicking a host stress that can render Mtb non-replicating) results in cell death.
