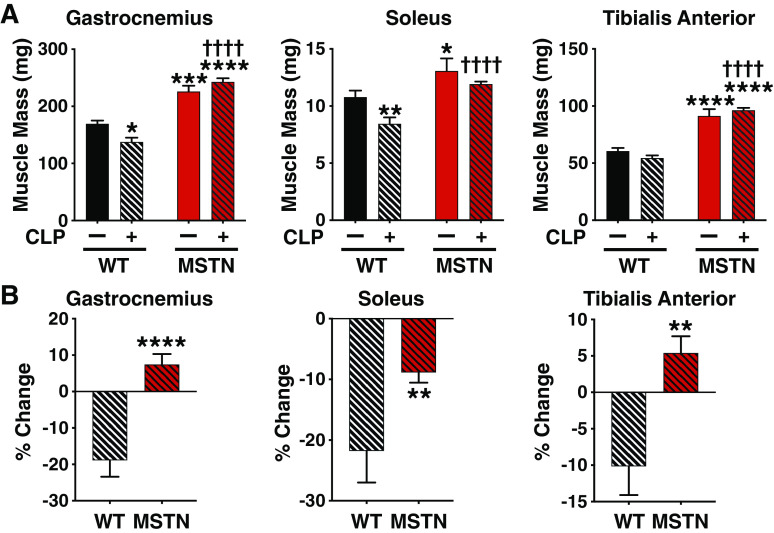
Figure 2.
Myostatin deficiency conferred resistance to sepsis-induced muscle mass loss in mice. A: the muscle mass of naïve mice and in septic mice was greater in myostatin-deficient (MSTN) mice than in body weight-matched wild-type (WT) mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 vs. WT mice without CLP, ††††P < 0.0001 vs. WT mice with CLP. B: cecum ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced percent changes in muscle mass were compared between myostatin-deficient (MSTN) and body weight-matched wild-type (WT) mice. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 vs. WT mice, WT mice without CLP: n = 7, WT mice with CLP: n = 8, MSTN mice without CLP: n = 7, MSTN mice with CLP: n = 18.