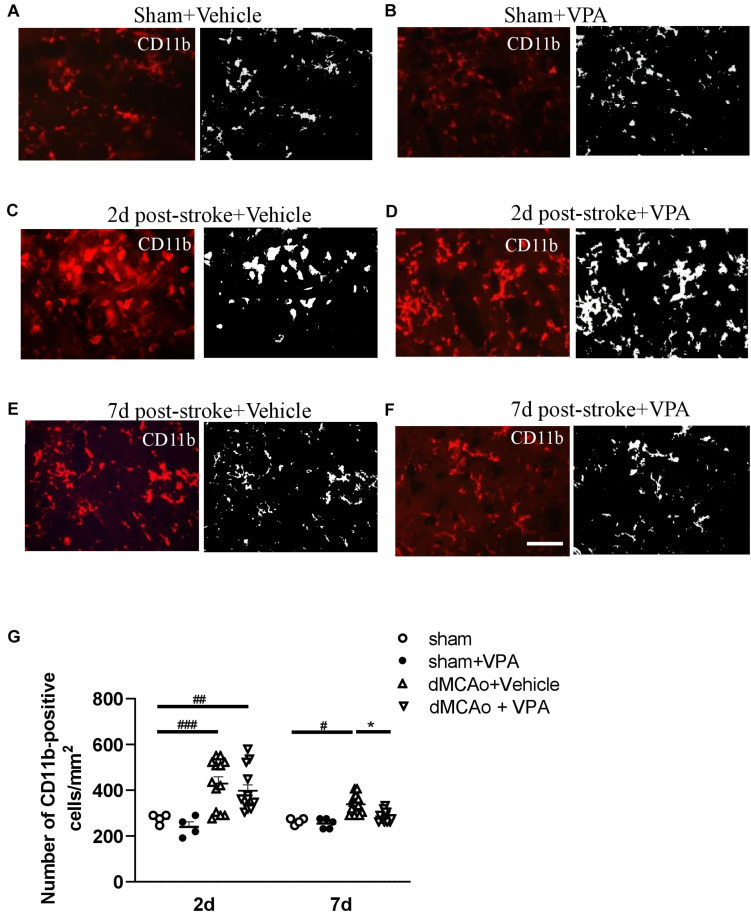
FIGURE 4.
Post-stroke intraperitoneal injection of VPA decreases the number of CD11b-positive cells in the peri-infarct cortex. (A–F) Representative photomicrographs of anti-CD11b immunofluorescent staining of the sham-operated cortex in vehicle-treated rats (A), sham-operated cortex in VPA-treated rats (B), peri-infarct cortex at 2 days after 90-min dMCAo in vehicle-treated rats (C), peri-infarct cortex at 2 days after 90-min dMCAo in VPA-treated rats (D), peri-infarct cortex at 7 days after 90-min dMCAo in vehicle-treated rats (E), and peri-infarct cortex at 7 days after 90-min dMCAo in VPA-treated rats (F). (G) Quantitation of CD11b-positive cells in the peri-infarct cortex at different time points showing accumulation of activated microglia/macrophages in the peri-infarct cortex at 2 and 7 days after ischemia. Original photomicrographs were subjected to a series of uniform Image J plugin protocols prior to conversion to binary images; binary images were then analyzed to calculate the number of CD11b-positive cells. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, and ###p < 0.001 indicate statistical difference between peri-infarct cortex and sham-operated cortex at each time point, Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test, following one-way ANOVA. *p < 0.05 indicates comparison with the dMCAo + vehicle group with two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni’s post hoc test. Five tissue sections per rat were used for the analysis (n = 8–10). Scale bar: 20 μm. The data represent mean ± SEM.