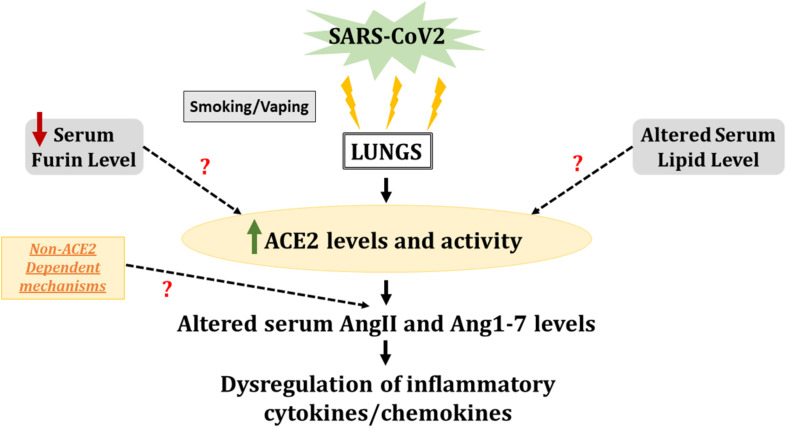
FIGURE 8.
SARS-CoV2 infection leads to increased ACE2 activity and serum cytokine levels in smokers. Serum samples from healthy individuals and COVID-19 positive patients with smoking history were compared for ACE2 activity and levels of inflammatory cytokines/chemokines. The results pointed toward increased ACE2 activity and altered AngII and Ang1–7 levels in the serum of COVID-19 patients as compared to normal individuals. The altered AngII and Ang1–7 levels could also be a result of non-ACE2 dependent mechanisms which is not studied here. Increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines/chemokines in COVID-19 positive patients with smoking history, indicates a heightened immune response on SARS-CoV2 infection in smokers. We also found evidence for lowered serum furin and altered lipid profiles amongst COVID-19 patients, which may or may not correlate with the ACE2 activity. These alterations can lead to heightened inflammatory response and lung remodeling with smoking/vaping history.