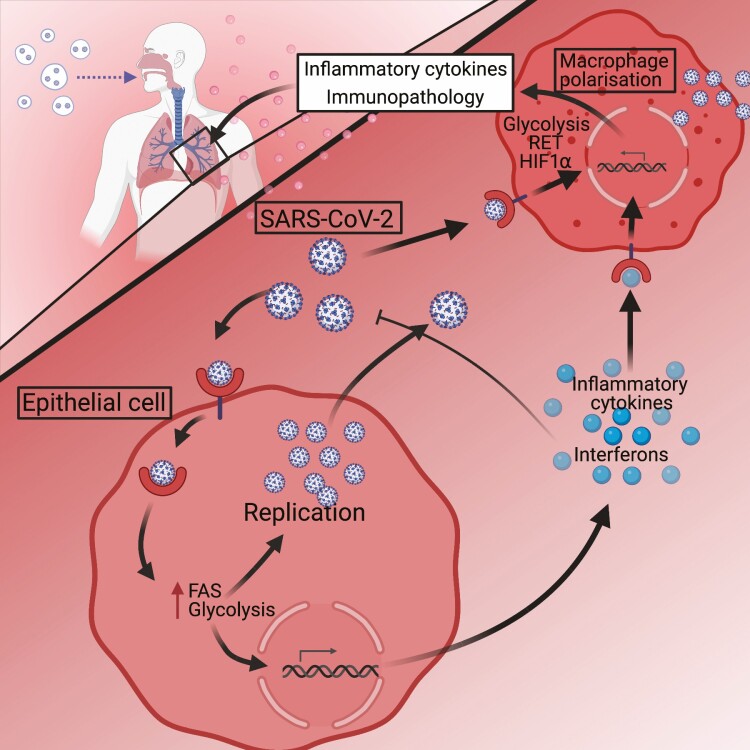
Figure 1.
Schematic of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the lung. SARS-CoV-2 infection of airway epithelial cells and macrophages causes an upregulation of glycolysis and fatty acid synthesis (FAS), to enable viral replication and release of SARS-CoV-2. Viral sensing by PRRs causes interferon production, while increased glycolysis and FAS induces inflammatory cytokine production. Macrophages can be infected by SARS-CoV-2 in the same mechanism or can be polarised by inflammatory cytokines produced by airway epithelial cells. M1-like polarisation of macrophages causes the production of inflammatory cytokines that contribute to the immunopathology seen in COVID-19. Created with Biorender.com.