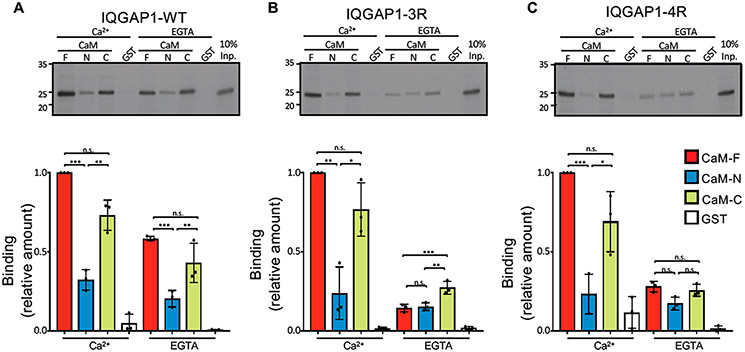
Figure 1.
Mutations of IQ3 and IQ4 motifs alter calmodulin binding. In vitro binding analysis of IQ domain constructs of IQGAP1. (A) The wild-type (WT) IQ domain (amino acids 717–916), (B) IQ3R, and (C) IQ4R were labeled with [35S]Met using TNT. Samples were incubated with purified recombinant GST-CaM constructs, namely, full-length (F, amino acids 1–148), N-half (N, amino acids 1–74), and C-half (C, amino acids 75–148) or GST alone. In the top panels, the bound proteins were resolved by SDS–PAGE and imaged by autoradiography. Input (Inp.) is 10% of the IQ domain used for the binding assay. Representative images of three independent experiments are shown. Autoradiographs were quantified with Li-Cor Image Studio Software. The amount of binding of each IQ domain was normalized to CaM-F in Ca2+. The graphs depict binding to CaM-F (red), CaM-N (blue), CaM-C (green), or GST (white). Data are means ± the standard deviation (n = 3). Significance was determined by ANOVA: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.0005; ns, not significant.